
我们提供安全,免费的手游软件下载!
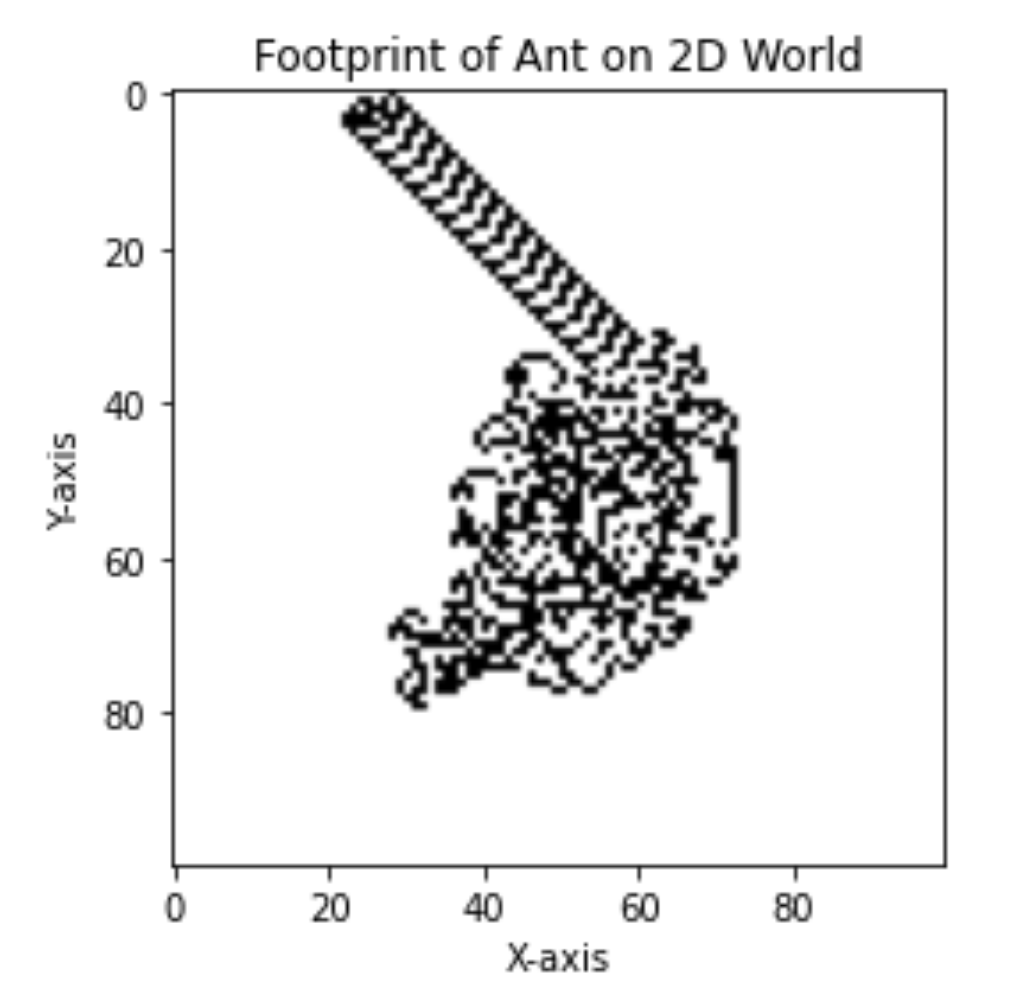
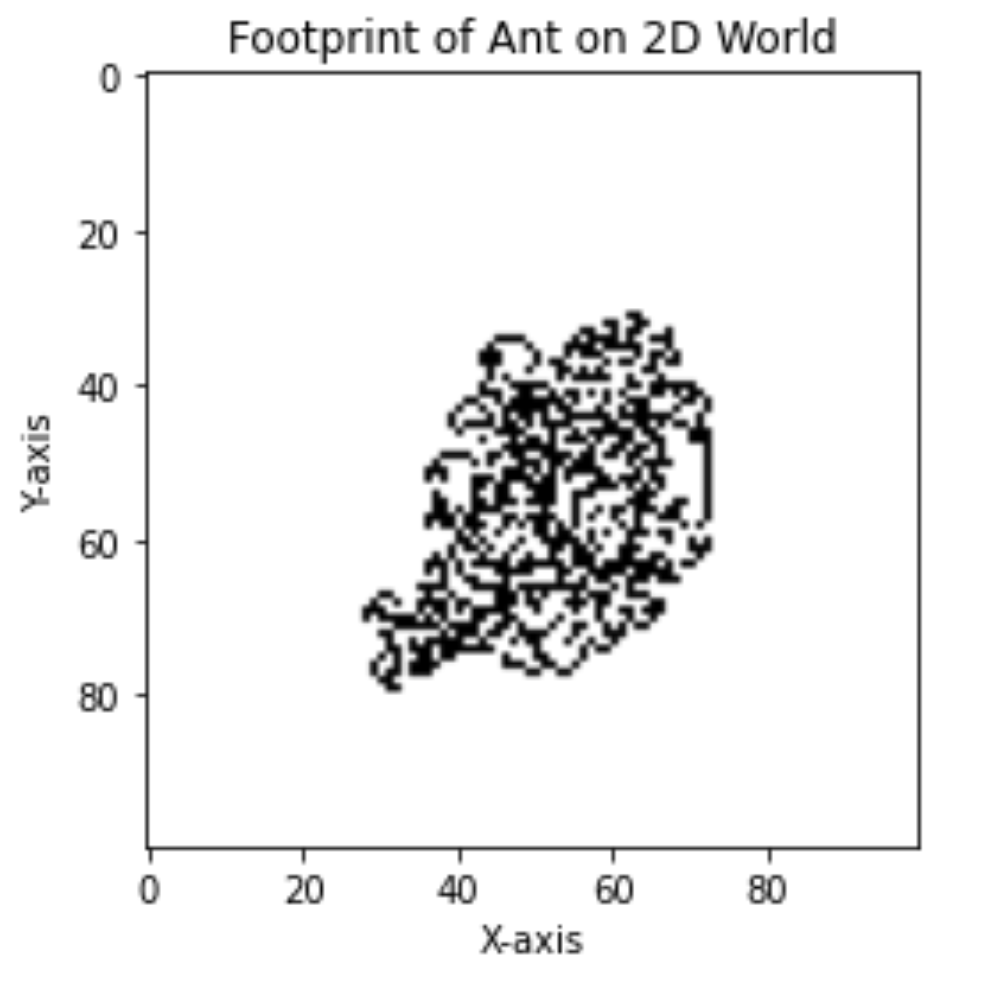
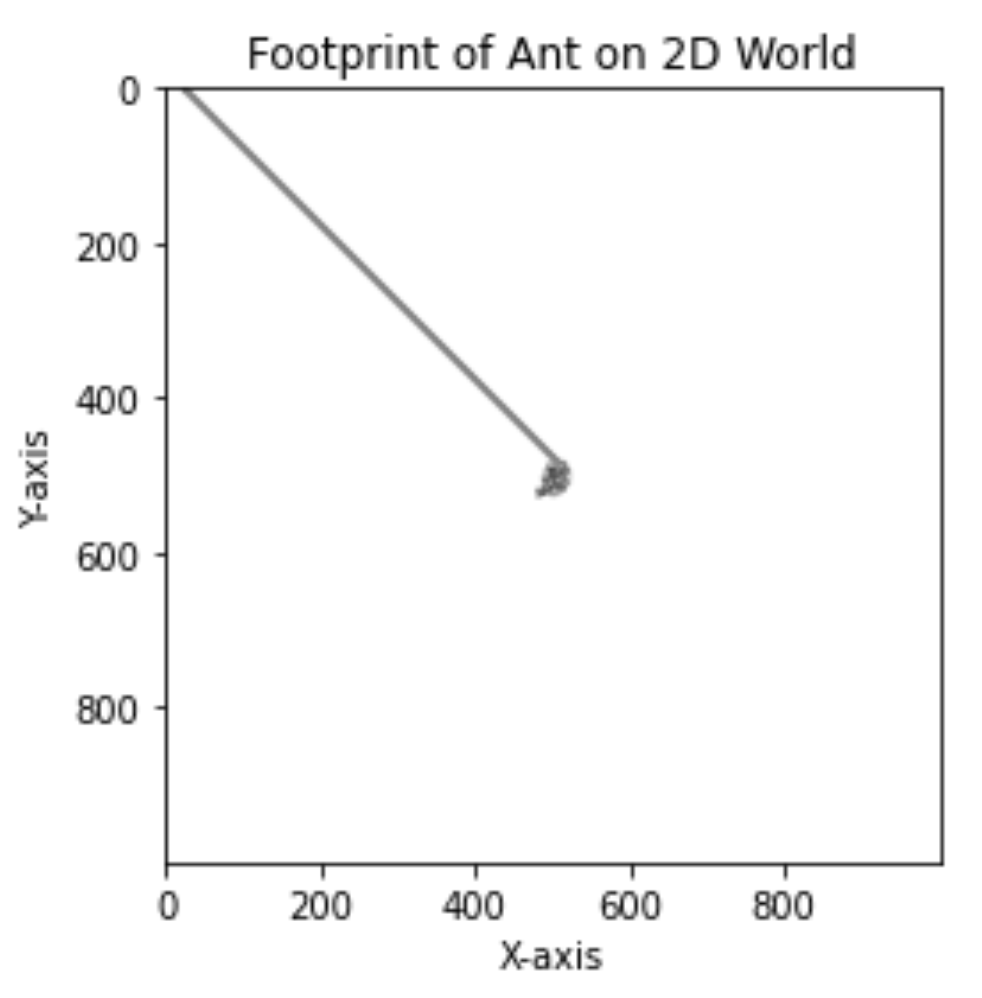
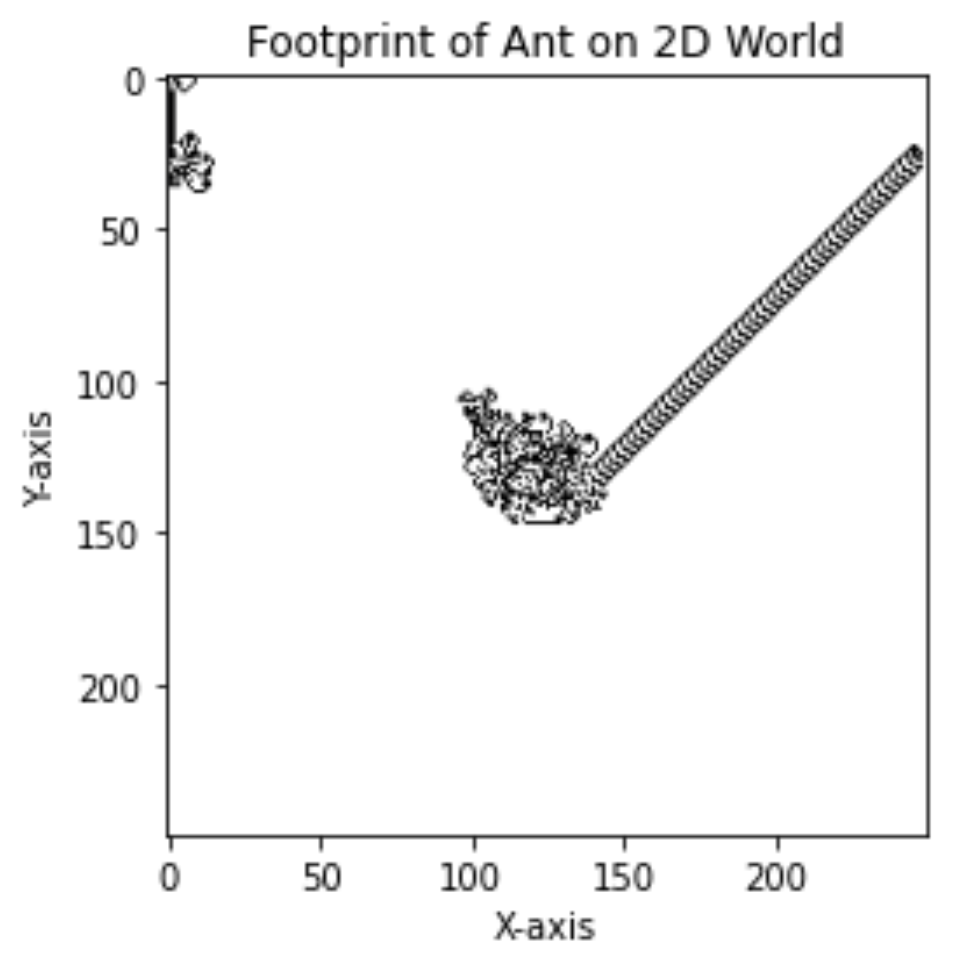
在一个1000*1000格子的棋盘上,有一只蚂蚁(ant),蚂蚁的爬行规则是:(1)如果蚂蚁所在的棋盘是白色的,则蚂蚁将所在格子设置为黑色,并向右边爬行一个格子。(2)如果蚂蚁所在的棋盘是黑色的,则蚂蚁将所在格子设置为白色,并向左边爬行一个格子。问:请显示蚂蚁爬行10000次后,棋盘的样子。
首先,我们需要创建一个棋盘类(Board)和一个蚂蚁类(Ant)。棋盘类包含一个二维数组表示棋盘的状态,以及一个方法用于显示棋盘。蚂蚁类包含蚂蚁当前的位置和爬行方法。
解析:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class Board:
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
# 创建初始棋盘,设置为全0的格子: 注意: 0 表示 白色,1表示 黑色
self.board = np.zeros((size, size))
def display(self):
# Create the figure and axes
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# Display the array as an image using imshow
# cmap='gray' sets the colormap to grayscale
# imshow 似乎 0 表示黑的,1 表示白色,因此,我这里用函数 np.logical_not()取反了一下
plt.imshow(np.logical_not(self.board), cmap='gray')
# Set axis labels and title (optional)
ax.set_xlabel("X-axis")
ax.set_ylabel("Y-axis")
ax.set_title("Footprint of Ant on 2D World")
# Display the plot
plt.show()
class Ant:
def __init__(self, board):
# 假定初始在 棋盘中央
self.x = board.size // 2
self.y = board.size // 2
# 假定初始方向朝上, 90度
self.direction = 90
def climb_one(self, board):
if self.direction == 0 : # right, 向右边爬行一格
self.x = self.x + 1
elif self.direction == 270: # down, 向下爬行一格
self.y = self.y - 1
elif self.direction == 180: # left, 向左爬行一格
self.x = self.x - 1
elif self.direction == 90: # up, 向上爬行一格
self.y = self.y + 1
# 处理一下跑出边界问题:
# 如果小于0, 则移动到最大值处, PS: 这样设置是有部分道理的,因为小于0 时候,direction是向左 或 向上的,
# 移动到最大值时候,ant 方向向内
# 如果大于最大值,则移动到0 处
if self.x == -1 :
self.x = board.size - 1
if self.y == -1 :
self.y = board.size - 1
if self.x == board.size - 1 :
self.x = 0
if self.y == board.size - 1 :
self.y = 0
def move(self, board):
if board.board[self.x][self.y] == 0: # 原来是白色0
# Step 1: 脚下格子设置为黑色1
board.board[self.x][self.y] = 1
# Step 2: 右转
self.direction = (self.direction - 90) % 360
# Step 3:爬行一格
self.climb_one(board)
else: # 原来是黑色1
# Step 1: 脚下格子设置为白色0
board.board[self.x][self.y] = 0
# Step 2:左 转
self.direction = (self.direction + 90) % 360
# Step 3:爬行一格
self.climb_one(board)
def run():
board = Board(250) # 棋盘大小设置
ant = Ant(board)
for _ in range(1000000): # 蚂蚁爬行次数
ant.move(board)
print("moving ......")
board.display()
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
热门资讯