
我们提供安全,免费的手游软件下载!
@
Give a perfect shot and go babe
别浪费 腐蚀所有虚伪
Crazy voices echoed in my head
想逃离 所有苦痛伤悲
把所有不良糟糕习惯全部戒除后
历经过无数次重击却依然抬起头
看见你失望落寞神情继而开始自我反思
感谢你们没放弃 握住我的手
Hold my hand
是时候开始飞行独立
Hold my hand
遵循前行者留的足迹
穿越过流言沙漠
忍受着漠视爆破
不管有任何warning依然升空永不坠落
If U 期待着胜利 存在的痕迹
歇斯底里 奢望着黎明 拒绝别的争议
从未放弃 在乱战后的废墟找寻记忆
终归在最泥泞的 沟壑里看到堕落距离
不管孤注还是继续 依靠信念维持秩序
努力探路哪怕崎岖 听着嘲弄不发一语
抓住机遇的followers 终将忘记了浮夸
寻找着真理看向前方
继续下一段的journey
They don't know the feel
真理在干涸的沙漠降落
该执着寻觅绿洲 燃起希望那团圣火
就算落寞 却记起 尊严不再 需要沉默
习惯堕落 在沉着里 选择假装 还是过错
你还坐在小时候的篝火旁
看天上的月亮还是那个模样
北斗星在指着你的前方
在夜里你也不会失去你的方向
不会再度感到迷茫
湖面倒映着天空是你心中的梦想
丢弃内心不安的彷徨
不会在任何寂静夜里孤单幻想流浪
你还坐在小时候的篝火旁(Give a perfect shot and go babe)
看天上的月亮还是那个模样(别浪费)
北斗星在指着你的前方(腐蚀所有虚伪)
在夜里你也不会失去你的方向
不会再度感到迷茫(Crazy voices echoed in my head)
湖面倒映着天空是你心中的梦想(想逃离)
丢弃内心不安的彷徨
不会在任何寂静夜里孤单幻想流浪
—————— 《篝火旁(再启程)》
什么是事务
在一个业务流程当中,通常需要多条DML(insert delete update) 语句共同联合才能完成,这多条DML语句必须同时成功,或者同时失败,这样才能保证数据的安全。
多条DML要么同时成功,要么同时失败,这叫做事务。事务(Transaction)
事务的四个处理过程:
- 第一步:开启事务(start transaction)
- 第二步:执行核心业务代码
- 第三步:提交事务(如果核心业务处理过程中没有出现异常)(commit transaction)
- 第四步:回滚事务(如果核心业务处理过程中出现异常)(rollback transaction)
事务的四个特性:
- 原子性:事务是最小的工作单元,不可再分
- 一致性:事务要求要么同时成功,要么同时失败,事务前和事务后的总量不变
- 隔离性:事务和事务之间因为有隔离性,才可以保证互不干扰
- 持久性:持久性是事务结束的标志。
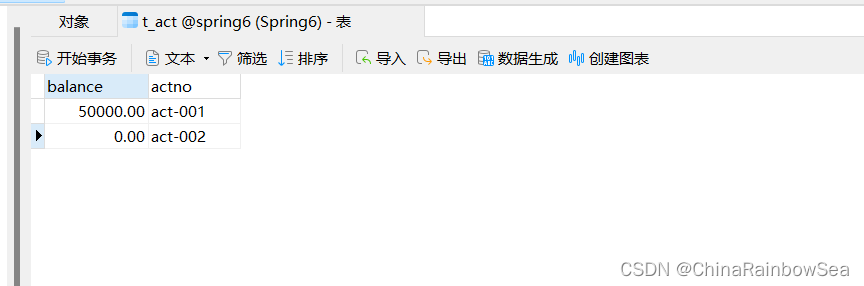
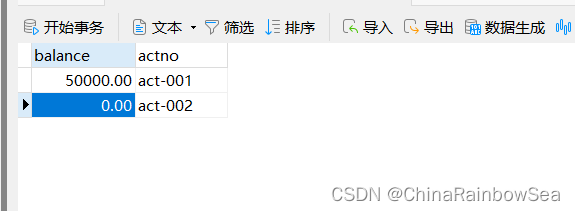
以银行账户转账为例学习事务,两个账户 act-001 和 act-002 。act-002 账户转账 10000,必须同时成功,或者同时失败,(一个减成功,一个加成功,这两条update 语句必须同时成功,或同时失败。)连接数据库的技术采用Spring 框架的JdbcTemplate.
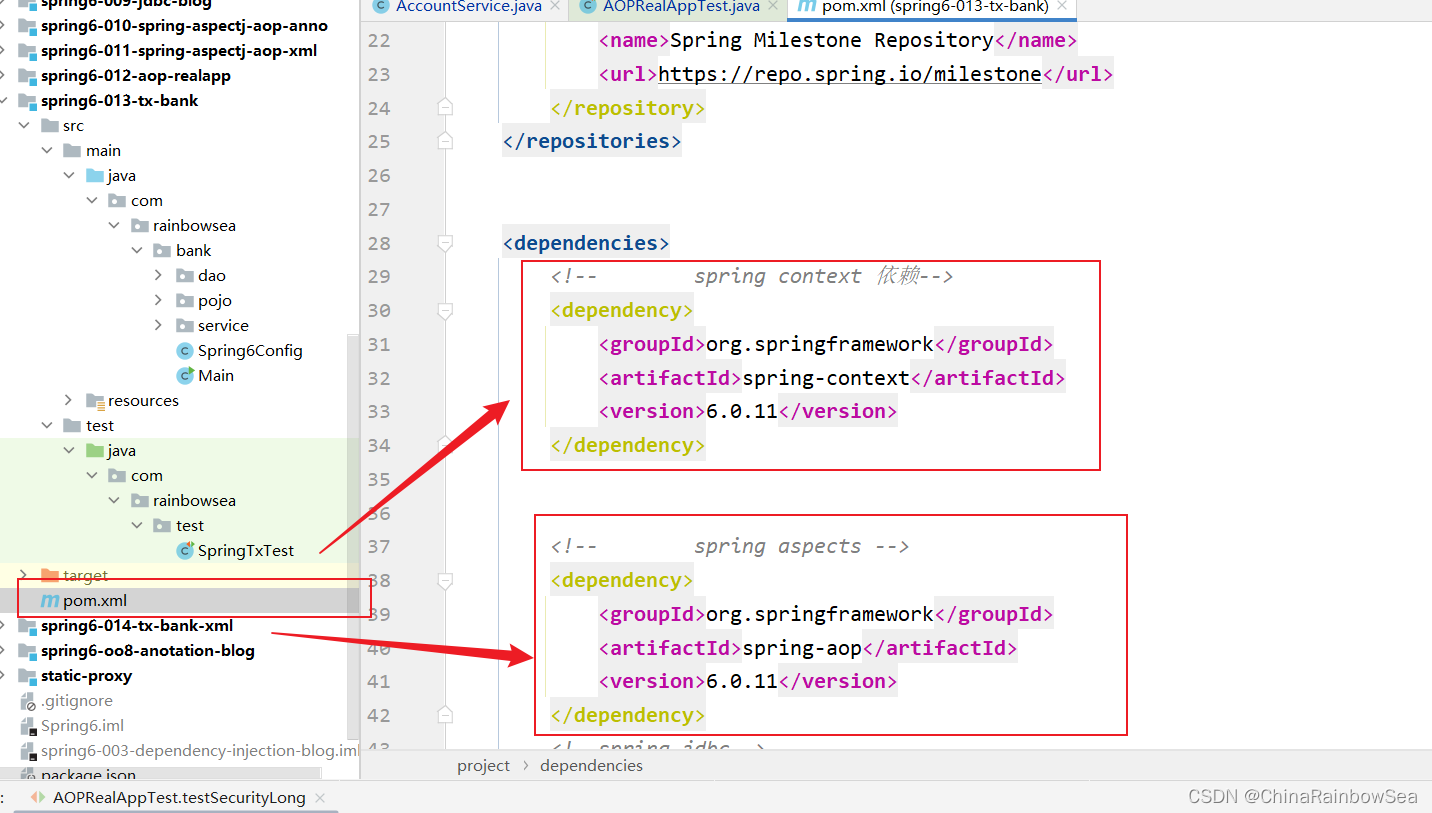
首先我在
pom.xml
当中先配置对应项目模块需要依赖的 jar包。
4.0.0
org.example
spring6-013-tx-bank
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
17
17
repository.spring.milestone
Spring Milestone Repository
https://repo.spring.io/milestone
org.springframework
spring-context
6.0.11
org.springframework
spring-aop
6.0.11
org.springframework
spring-jdbc
6.0.11
org.springframework
spring-aspects
6.0.11
mysql
mysql-connector-java
8.0.30
com.alibaba
druid
1.2.13
jakarta.annotation
jakarta.annotation-api
2.1.1
junit
junit
4.13.2
test
org.apache.logging.log4j
log4j-core
2.19.0
org.apache.logging.log4j
log4j-slf4j2-impl
2.19.0
com.powernode.bank.pojo
com.powernode.bank.service
com.powernode.bank.service.impl
com.powernode.bank.dao
com.powernode.bank.dao.impl
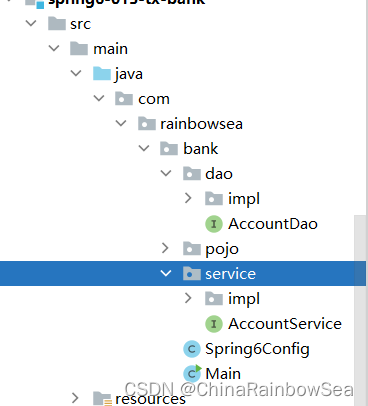
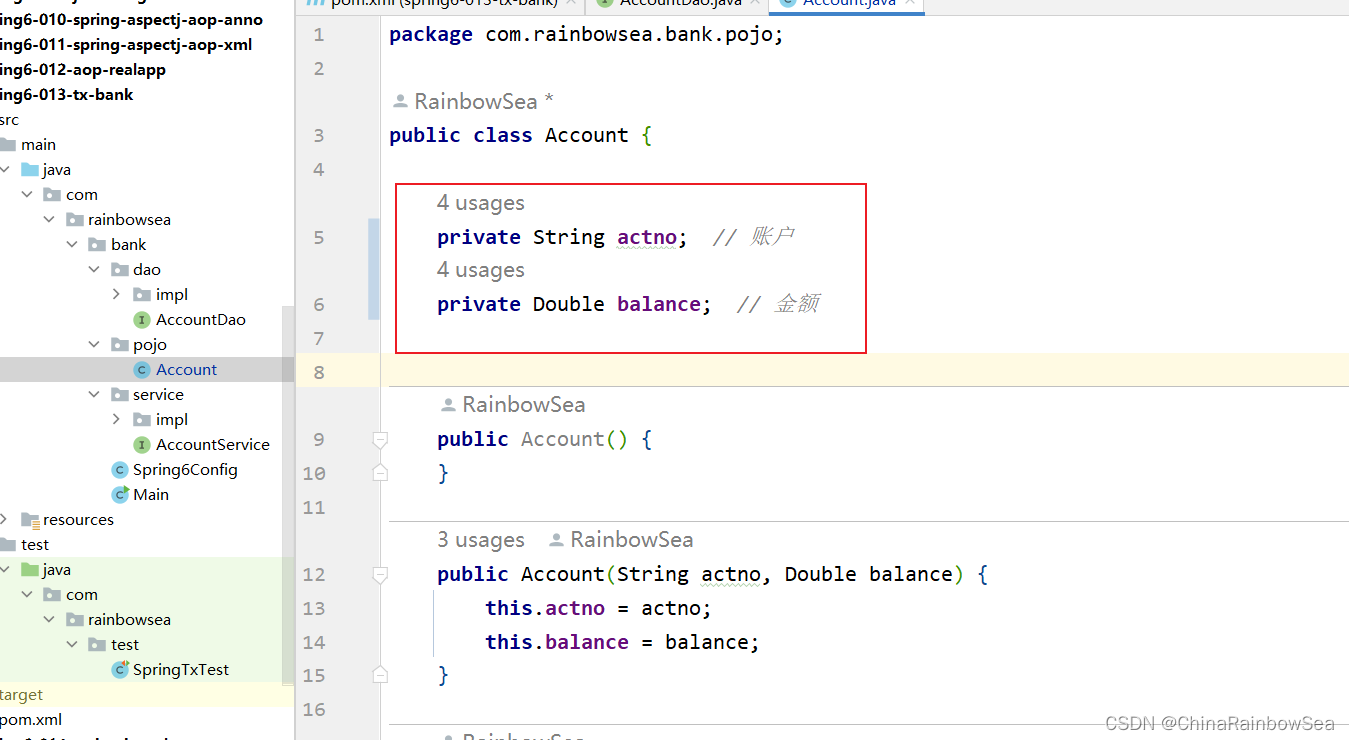
package com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo;
public class Account {
private String actno; // 账户
private Double balance; // 金额
public Account() {
}
public Account(String actno, Double balance) {
this.actno = actno;
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"actno='" + actno + '\'' +
", balance=" + balance +
'}';
}
public String getActno() {
return actno;
}
public void setActno(String actno) {
this.actno = actno;
}
public Double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(Double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
首先定义规范,持久层的规范,通过接口(interface) 来定义约束。
转账:首先我们需要查询对应账户上是否有该满足的余额;如果够,我们就需要更新数据(修改数据);所以定义两个方法就行:根据账户查询,根据账户修改
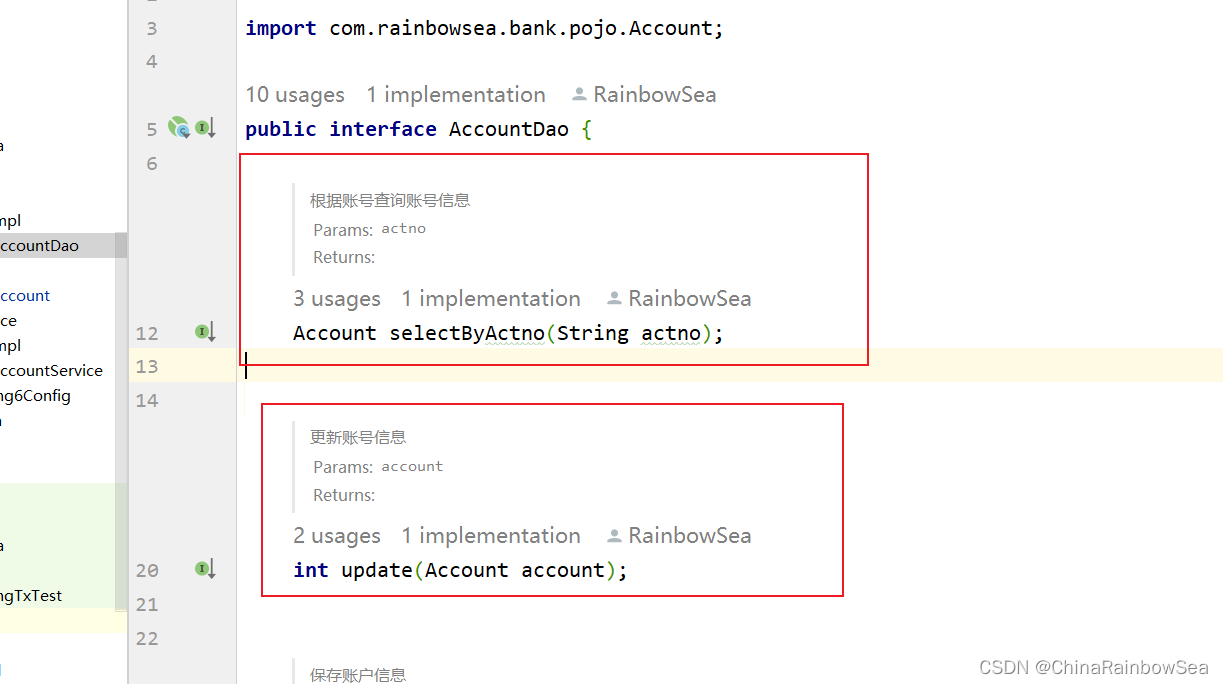
package com.rainbowsea.bank.dao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* 根据账号查询账号信息
* @param actno
* @return
*/
Account selectByActno(String actno);
/**
* 更新账号信息
* @param account
* @return
*/
int update(Account account);
}
根据该接口,编写对应持久层的实现类
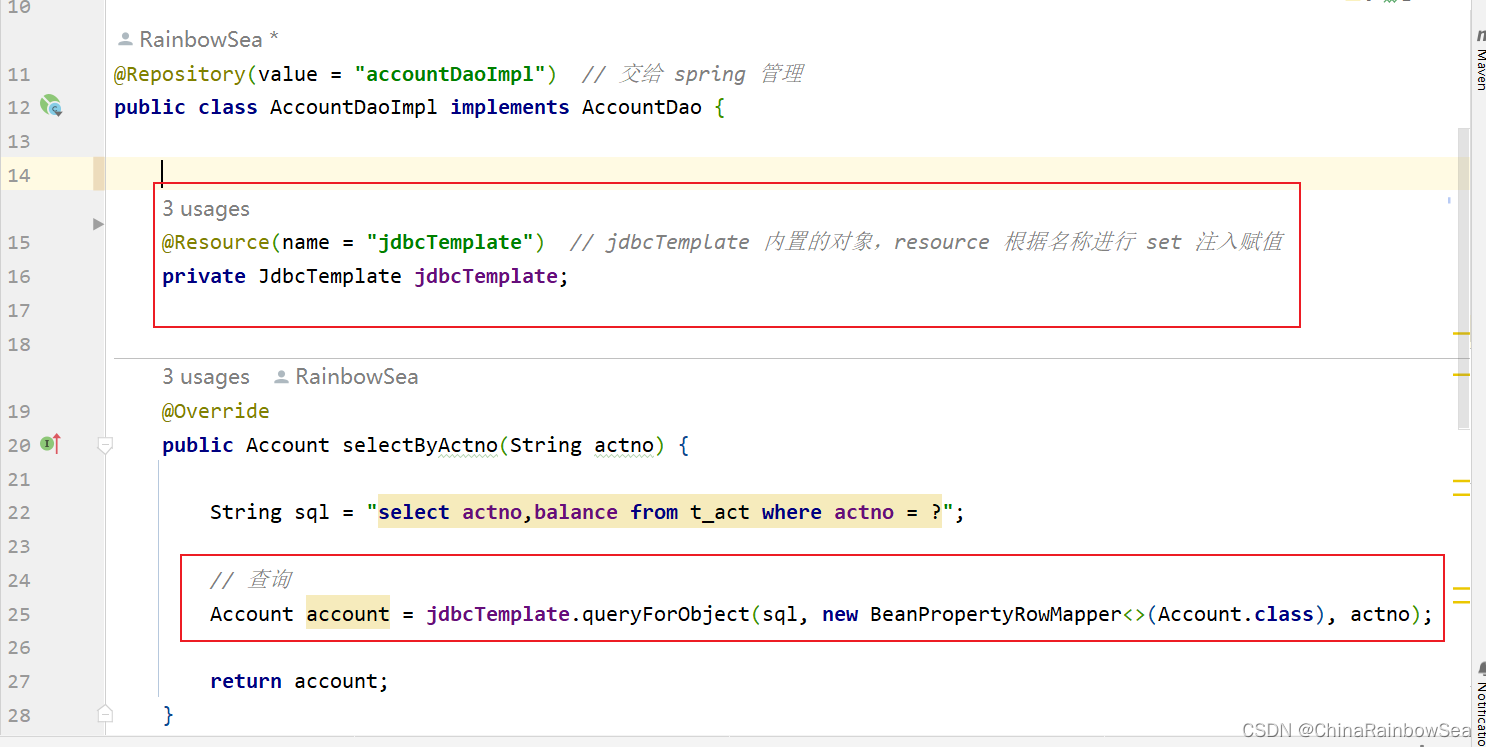
package com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository(value = "accountDaoImpl") // 交给 spring 管理
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
@Resource(name = "jdbcTemplate") // jdbcTemplate 内置的对象,resource 根据名称进行 set 注入赋值
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public Account selectByActno(String actno) {
String sql = "select actno,balance from t_act where actno = ?";
// 查询
Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Account.class), actno);
return account;
}
@Override
public int update(Account account) {
String sql = "update t_act set balance = ? where actno = ?";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, account.getBalance(), account.getActno());
return count;
}
}
首先定义规范,业务层的规范,通过接口(interface) 来定义约束。
定义一个进行转账操作的业务
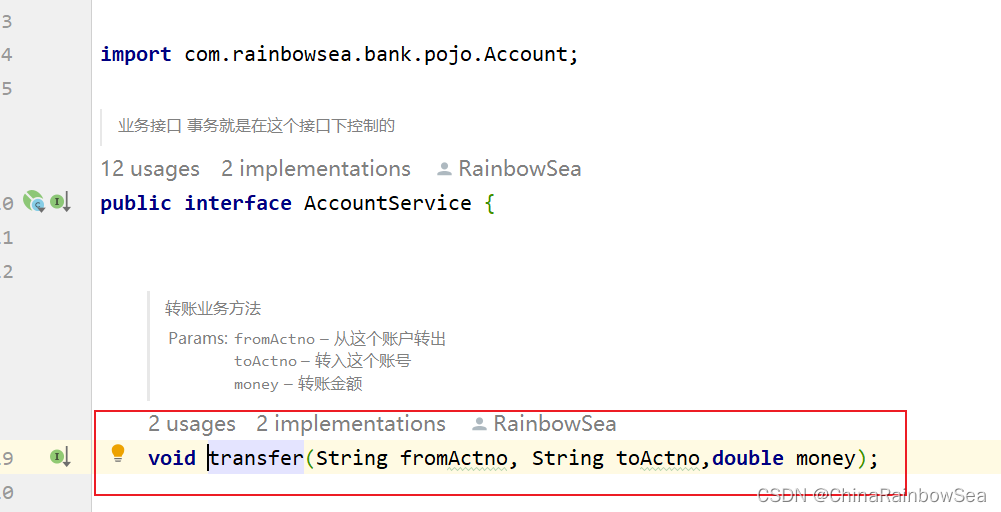
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
/**
* 业务接口
* 事务就是在这个接口下控制的
*/
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 转账业务方法
* @param fromActno 从这个账户转出
* @param toActno 转入这个账号
* @param money 转账金额
*/
void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno,double money);
}
根据该接口,编写对应业务层的实现类。
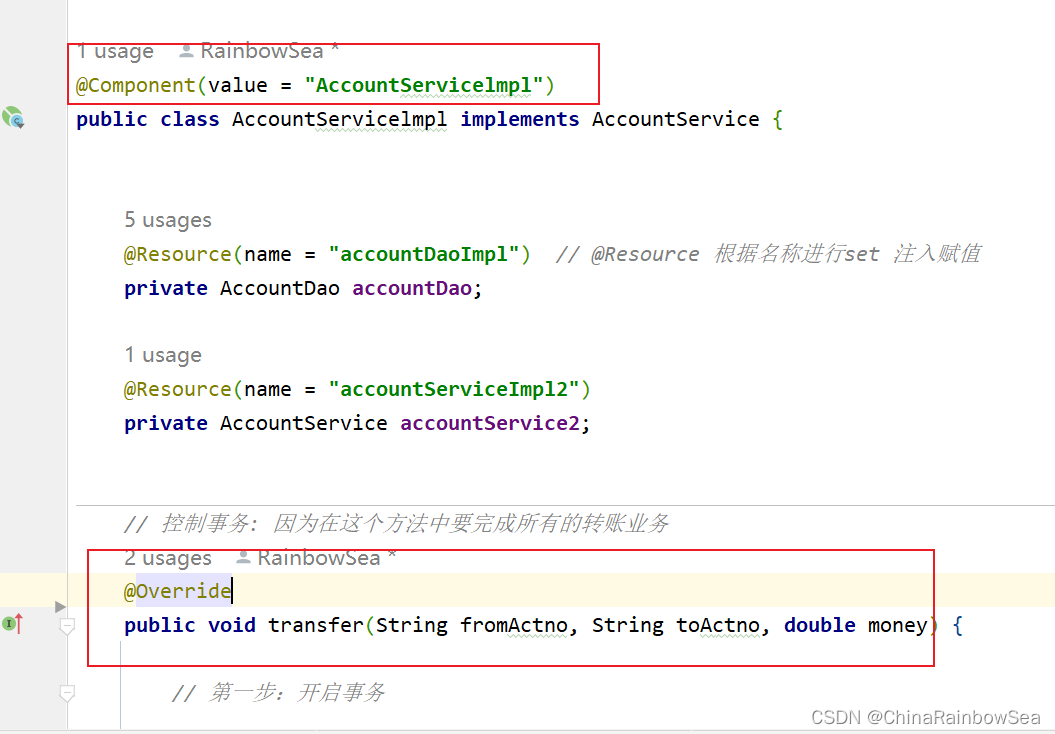
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.service.AccountService;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Component(value = "AccountServicelmpl")
public class AccountServicelmpl implements AccountService {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl") // @Resource 根据名称进行set 注入赋值
private AccountDao accountDao;
// 控制事务: 因为在这个方法中要完成所有的转账业务
@Override
public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) {
// 第一步:开启事务
// 第二步:执行核心业务逻辑
// 查询转出账号的余额是否充足
Account fromAct = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno);
if (fromAct.getBalance() < money) {
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足,转账失败");
// 第三步:回滚事务
}
// 余额充足
Account toAct = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno);
// 将内存中两个对象的余额先修改一下
fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance() - money);
toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance() + money);
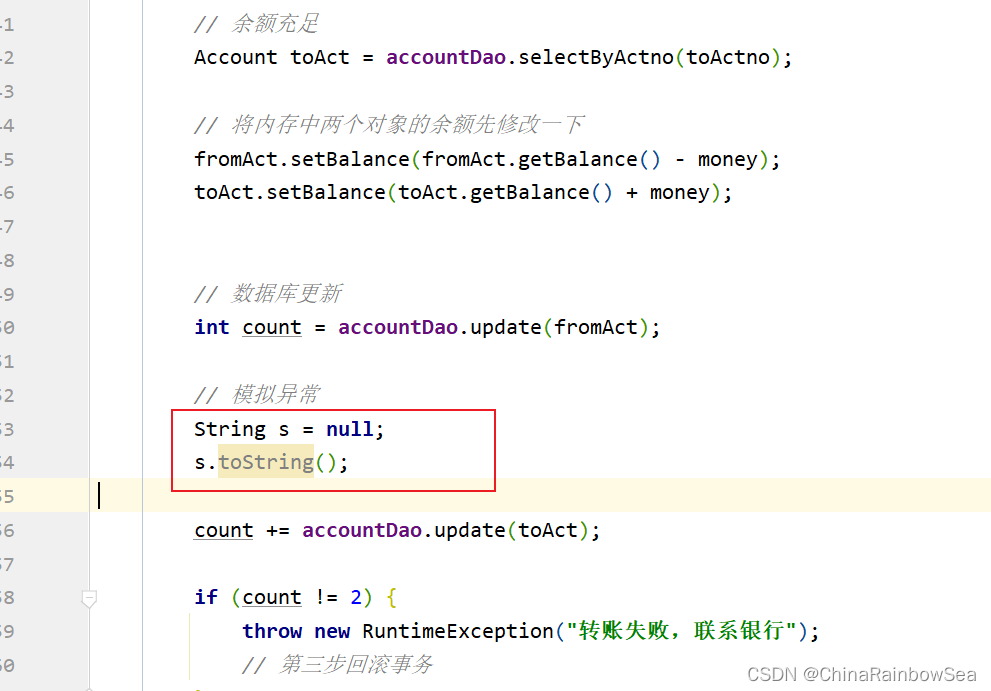
// 数据库更新
int count = accountDao.update(fromAct);
// 模拟异常
String s = null;
s.toString();
count += accountDao.update(toAct);
if (count != 2) {
throw new RuntimeException("转账失败,联系银行");
// 第三步回滚事务
}
// 第三步:如果执行业务流程过程中,没有异常,提交事务
// 第四五:如果执行业务流程过程中,有异常,回滚事务
}
}
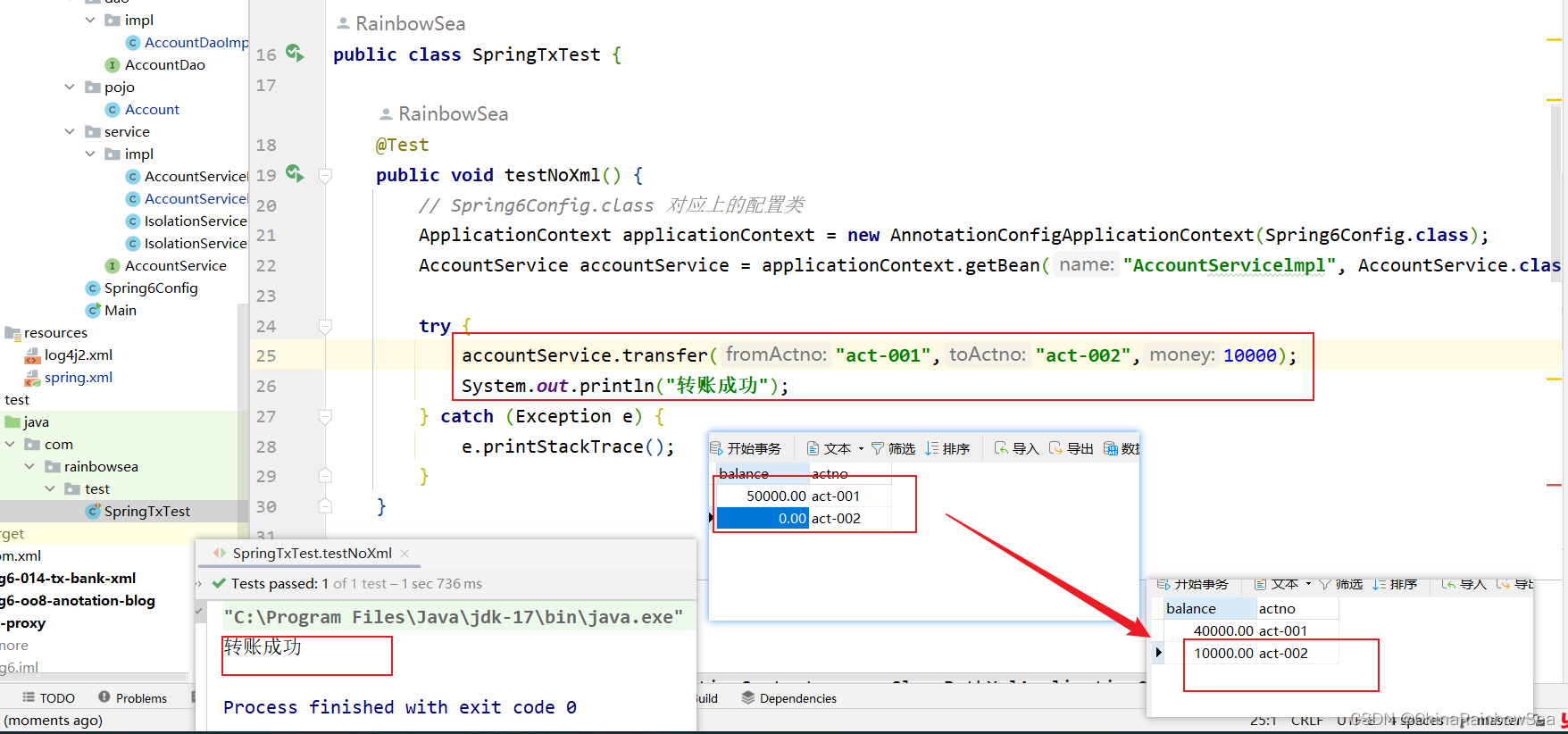
public class SpringTxTest {
@Test
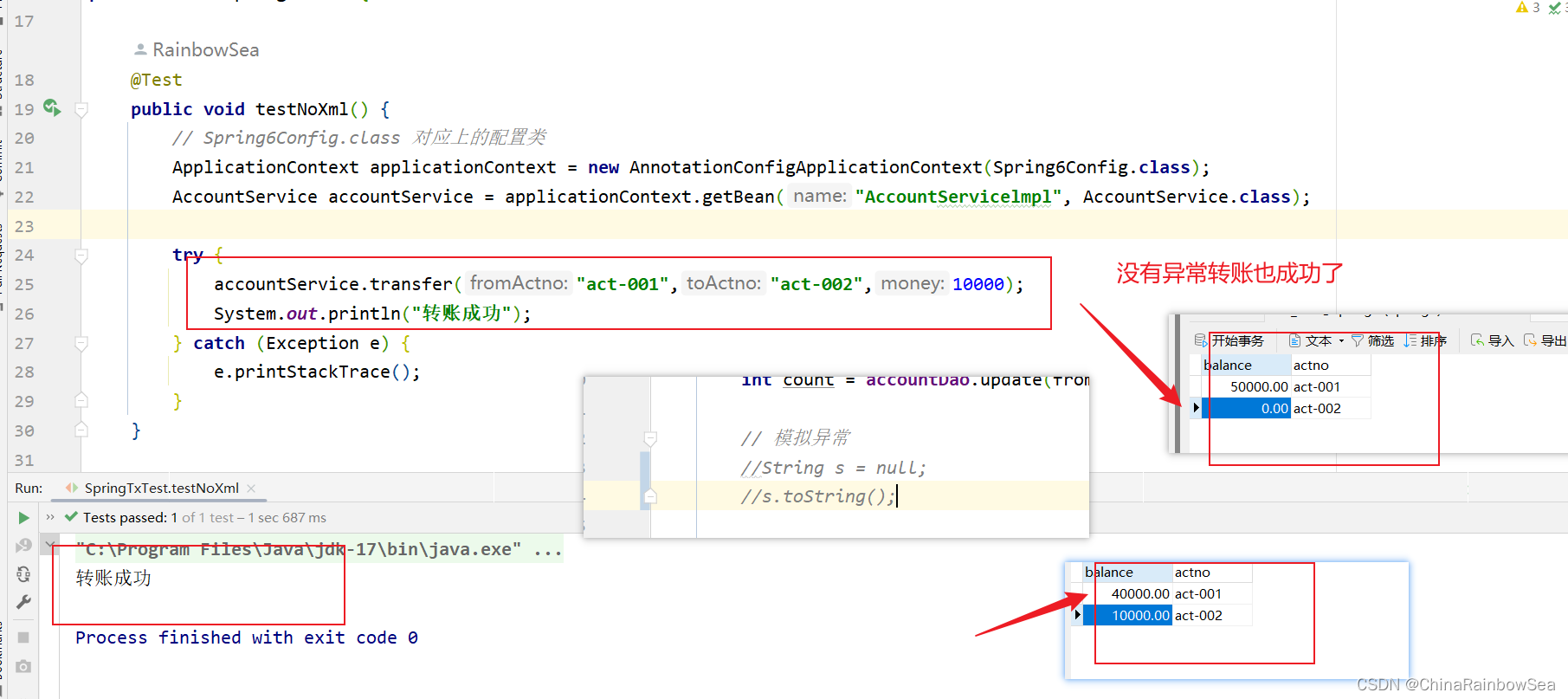
public void testNoXml() {
// Spring6Config.class 对应上的配置类
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Spring6Config.class);
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("AccountServicelmpl", AccountService.class);
try {
accountService.transfer("act-001","act-002",10000);
System.out.println("转账成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
通过在 AccountServicelmpl 业务层模拟,null 指针异常,看转账是否成功。
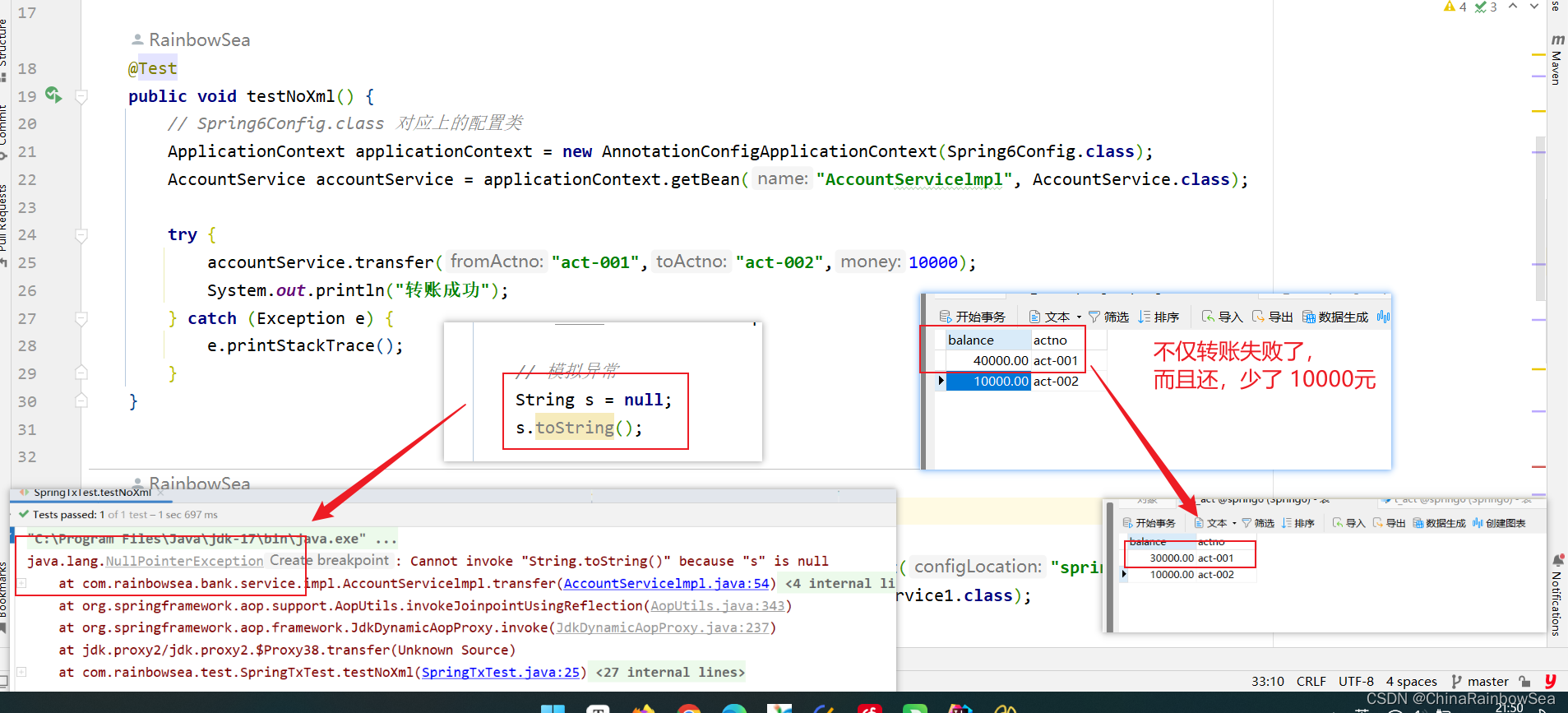
public class SpringTxTest {
@Test
public void testNoXml() {
// Spring6Config.class 对应上的配置类
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Spring6Config.class);
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("AccountServicelmpl", AccountService.class);
try {
accountService.transfer("act-001","act-002",10000);
System.out.println("转账成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
编程式事务:
声明式事务:
Spring 对事务的管理底层实现方式是基于 AOP实现的,采用 AOP的方式进行了封装,所以Spring 专门针对事务开发了一套API,API的核心接口如下:
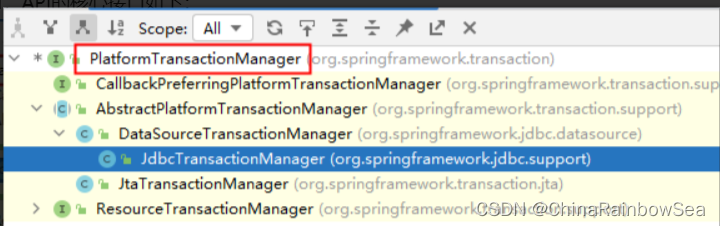
PlatformTransactionManager接口:spring 事务管理器的核心接口,在Spring6中它有两个实现:
DataSourceTransactionManager:支持JdbcTemplate、MyBatis、Hibernate等事务管理。
JtaTransactionManager:支持分布式事务管理。
如果要在Spring6中使用 JdbcTemplate,就要使用 DataSourceTransactionManager 来管理事务。(Spring 内置写好了,可以直接用)
第一步:
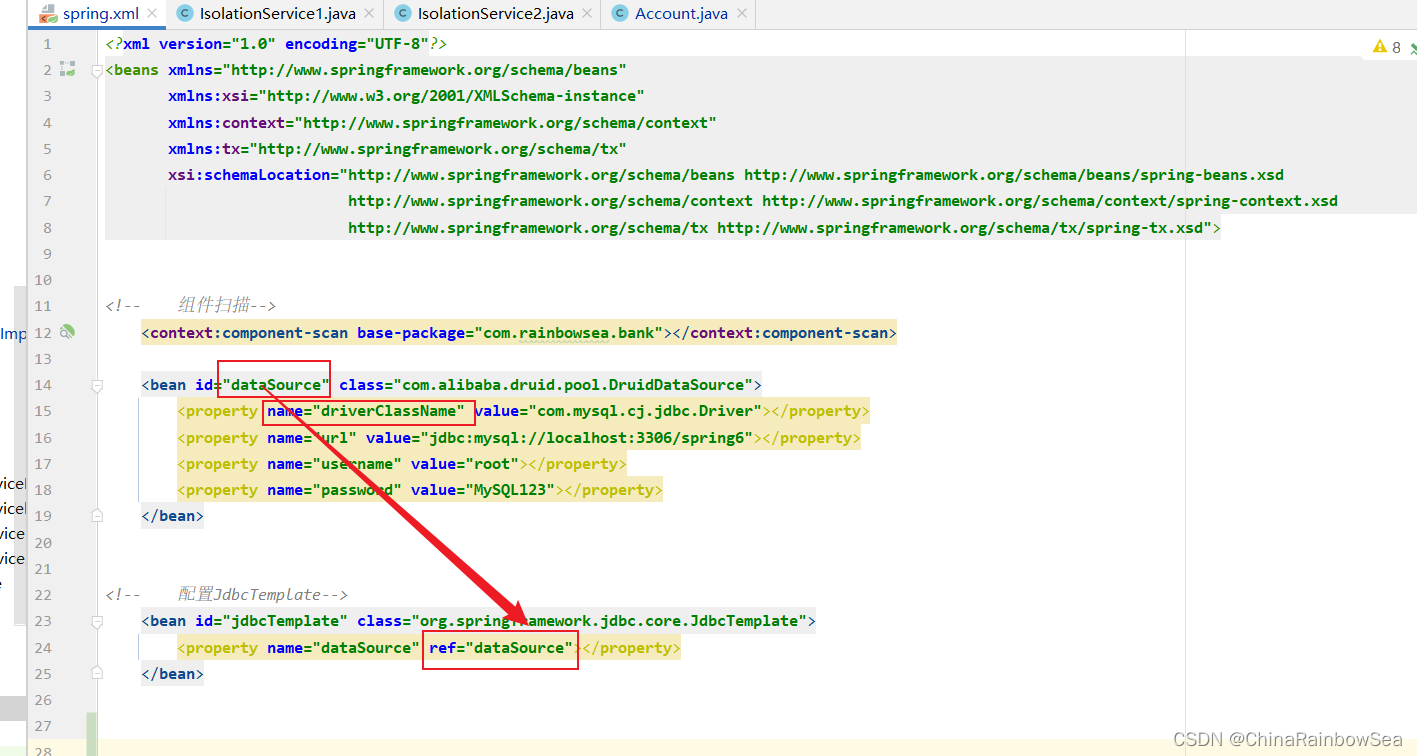
在
spring.xml
配置文件中配置事务管理器。
配置事务管理器,需要根据对应数据源里面的账户密码等信息,管理连接数据库,从而开启事务(开启事务,提交事务,回滚事务)等操作
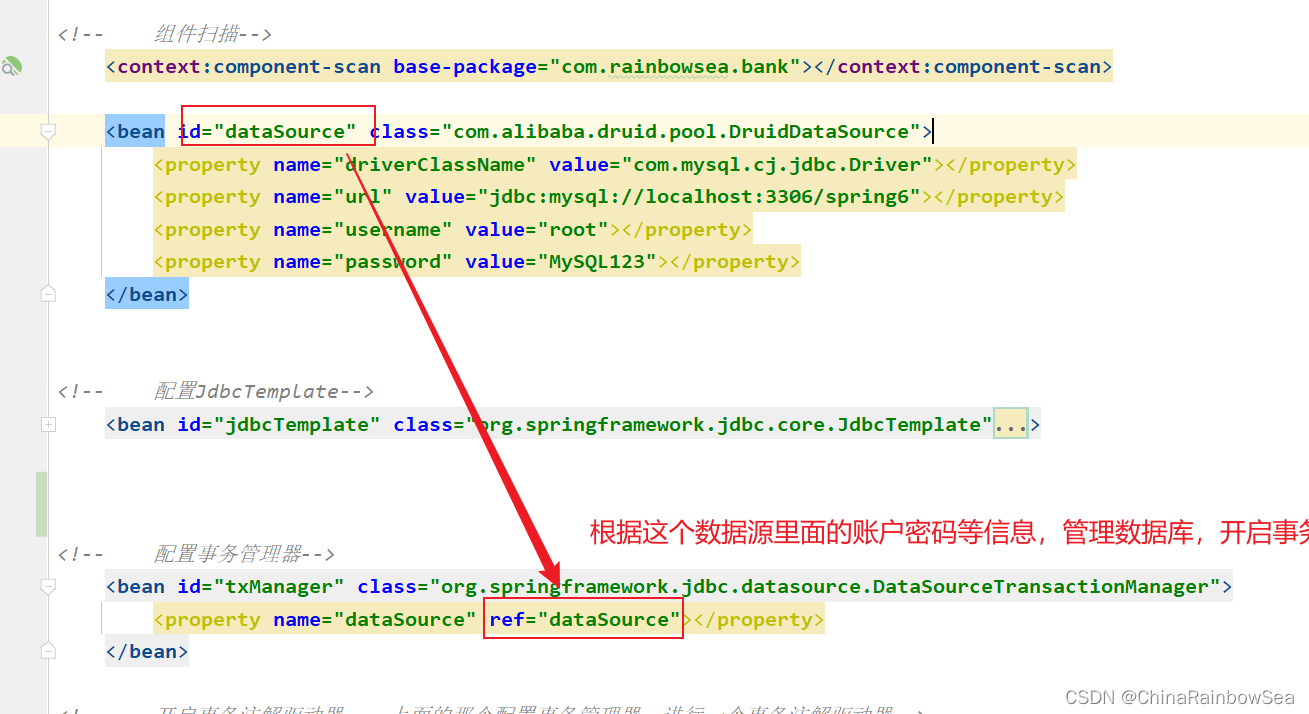
第二步: 在spring配置文件中引入tx命名空间。
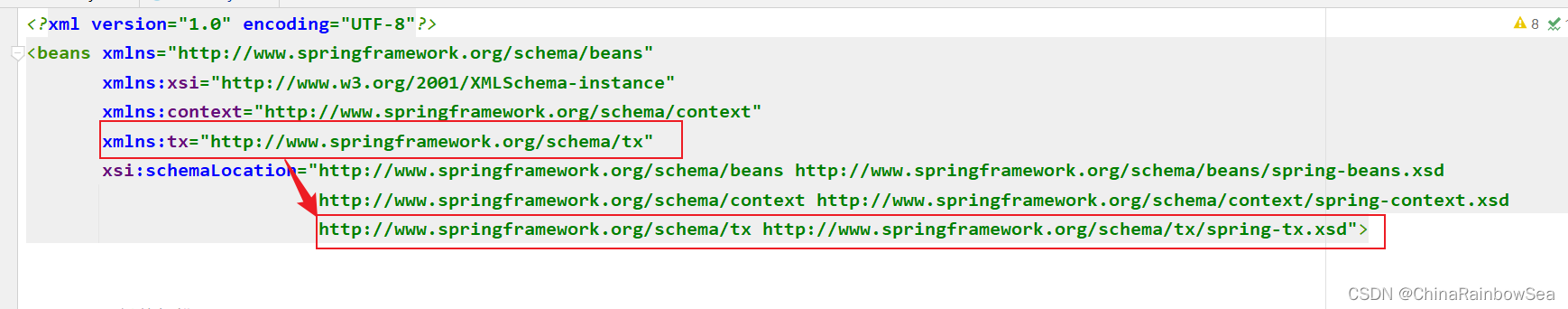
第三步:
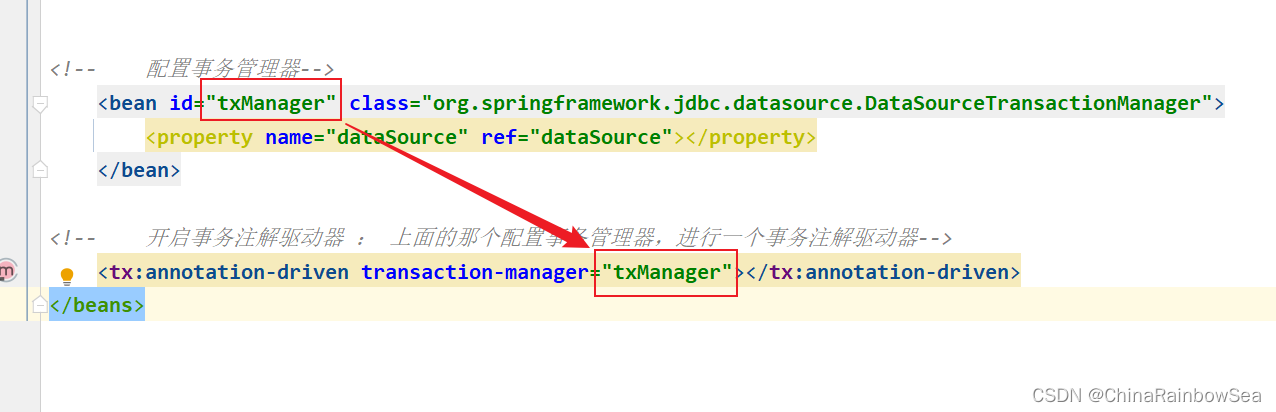
在
spring.xml
配置文件中配置“事务注解驱动器”,开始注解的方式控制事务。
是通过上面配置的 事务管理器 进行一个事务注解驱动器的 开启 。因为该事务管理器当中存储着对应数据库的账户和密码等信息(数据源)
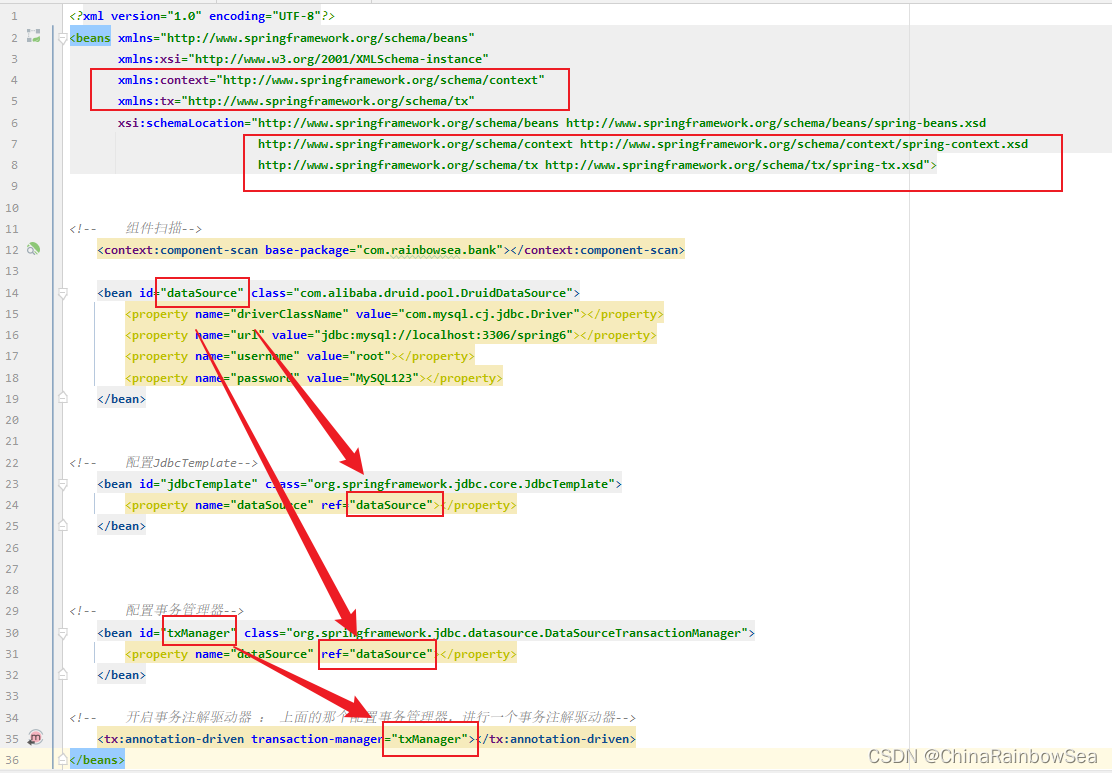
完整的
spring.xml
配置信息如下:
第四步: 在service类上或方法上添加@Transactional注解
- 在类上添加该@Transactional 注解,则表示该类中所有的方法都有事务了(都进行了事务上的控制,回滚了)
- 在某个方法上添加@Transactional注解,则表示只有这个方法使用了事务(进行了事务上的控制,回滚)其他的方法,并没有进行事务上的控制。
一般加入了事务的同时,也需要交给Spring IOC 容器进行管理 。
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.service.AccountService;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Component(value = "AccountServicelmpl")
@Transactional
public class AccountServicelmpl implements AccountService {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl") // @Resource 根据名称进行set 注入赋值
private AccountDao accountDao;
// 控制事务: 因为在这个方法中要完成所有的转账业务
@Override
public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) {
// 第一步:开启事务
// 第二步:执行核心业务逻辑
// 查询转出账号的余额是否充足
Account fromAct = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno);
if (fromAct.getBalance() < money) {
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足,转账失败");
// 第三步:回滚事务
}
// 余额充足
Account toAct = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno);
// 将内存中两个对象的余额先修改一下
fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance() - money);
toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance() + money);
// 数据库更新
int count = accountDao.update(fromAct);
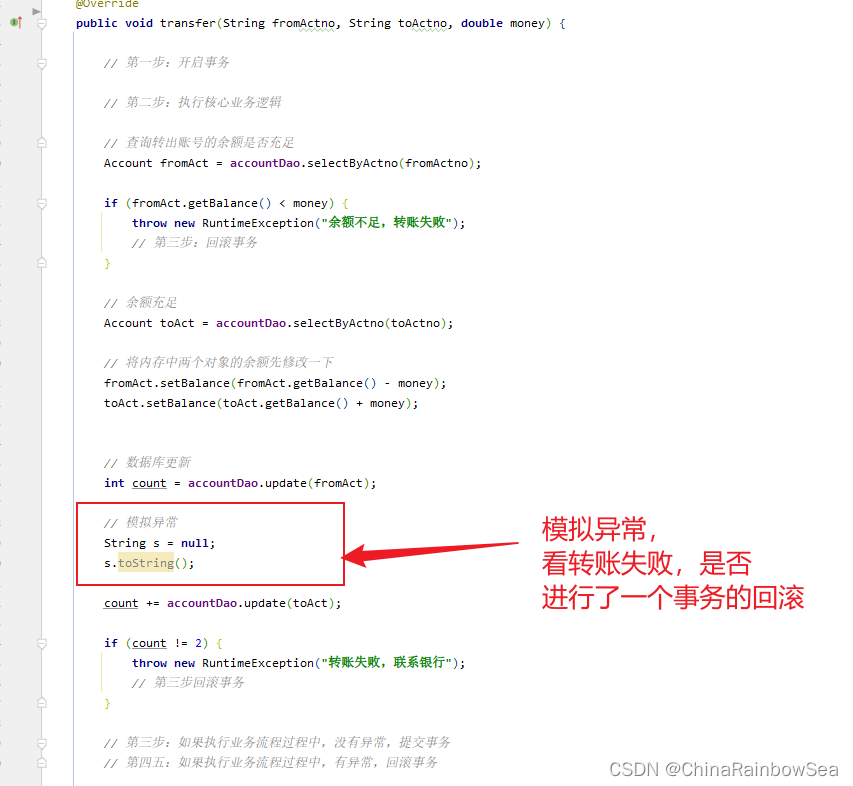
// 模拟异常
String s = null;
s.toString();
count += accountDao.update(toAct);
if (count != 2) {
throw new RuntimeException("转账失败,联系银行");
// 第三步回滚事务
}
// 第三步:如果执行业务流程过程中,没有异常,提交事务
// 第四五:如果执行业务流程过程中,有异常,回滚事务
}
}
运行测试:
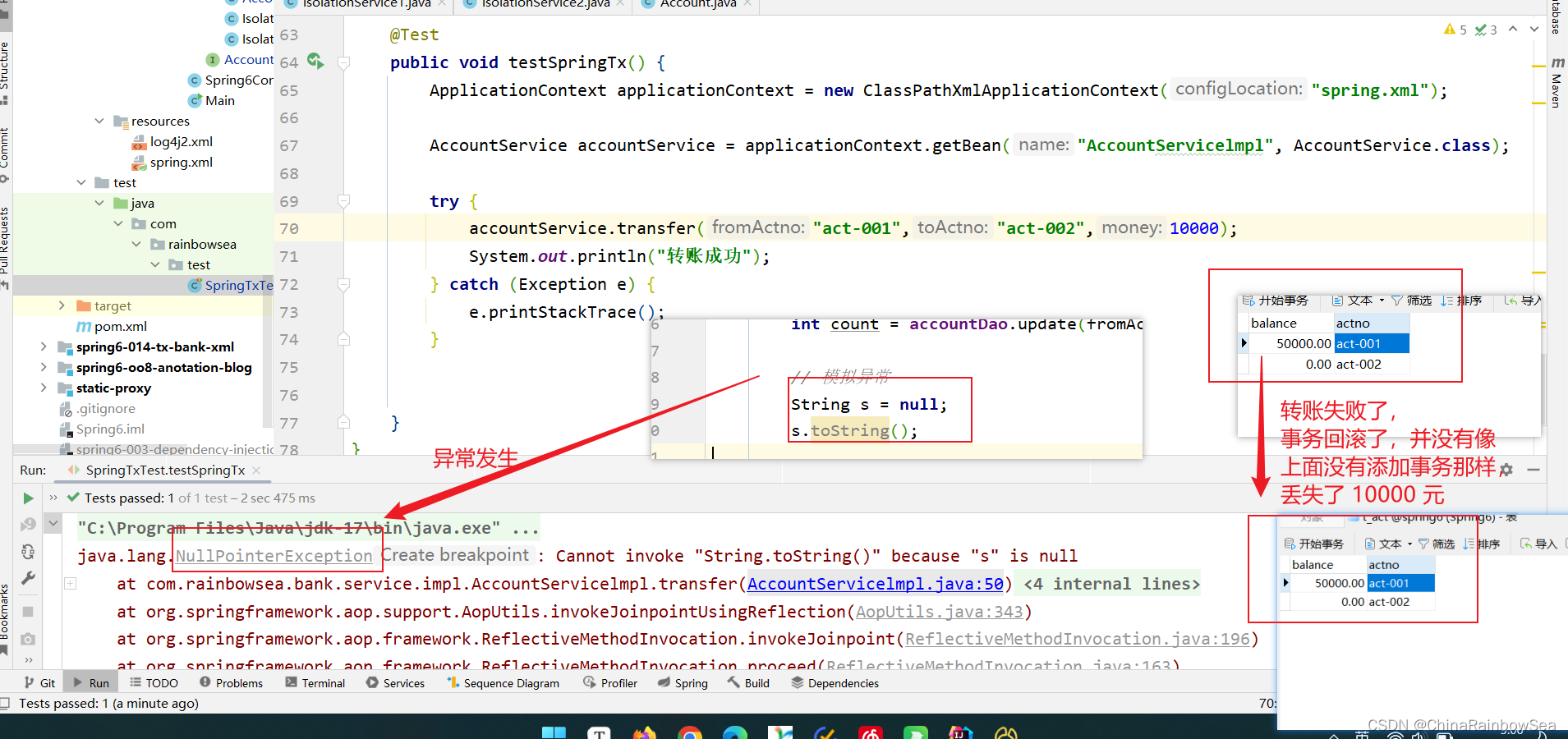
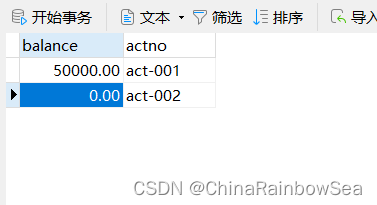
虽然出现异常了,再次查看数据库表中数据:通过测试,发现数据没有变化,事务起作用了。
@Test
public void testSpringTx() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("AccountServicelmpl", AccountService.class);
try {
accountService.transfer("act-001","act-002",10000);
System.out.println("转账成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
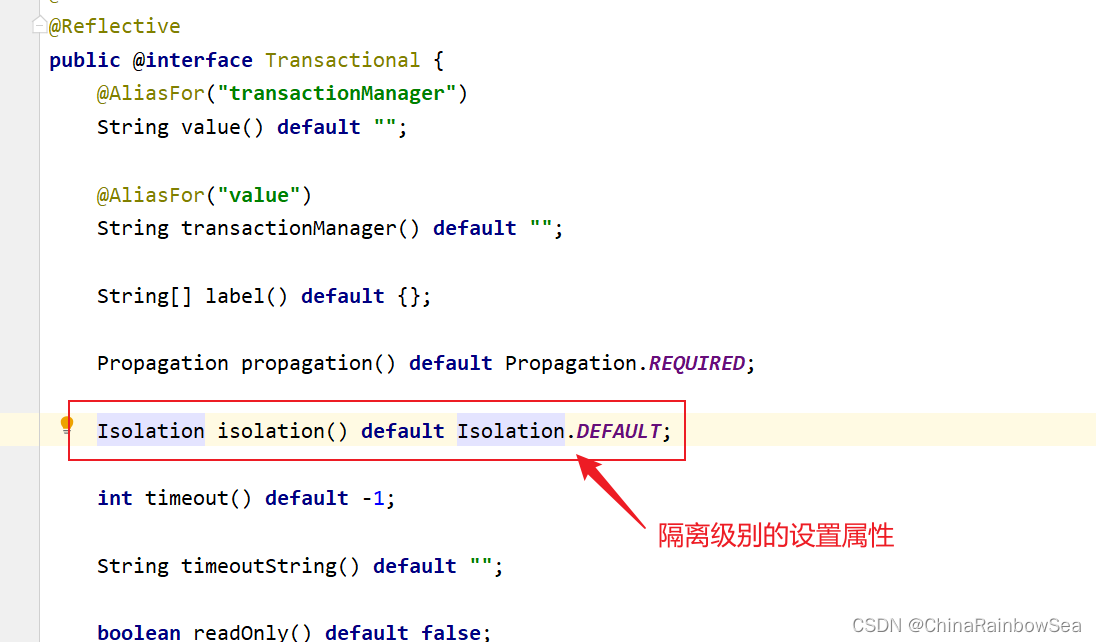
Spring 当中事务的属性,其实就是: @Transactional 注解当中的属性。
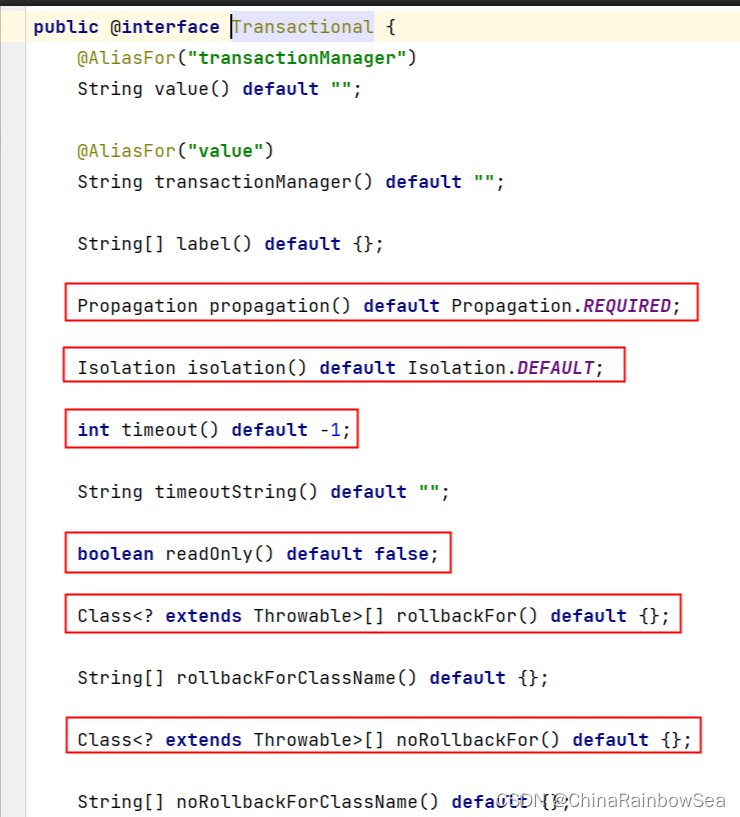
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.transaction.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.aot.hint.annotation.Reflective;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
@Reflective
public @interface Transactional {
@AliasFor("transactionManager")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String transactionManager() default "";
String[] label() default {};
Propagation propagation() default Propagation.REQUIRED;
Isolation isolation() default Isolation.DEFAULT;
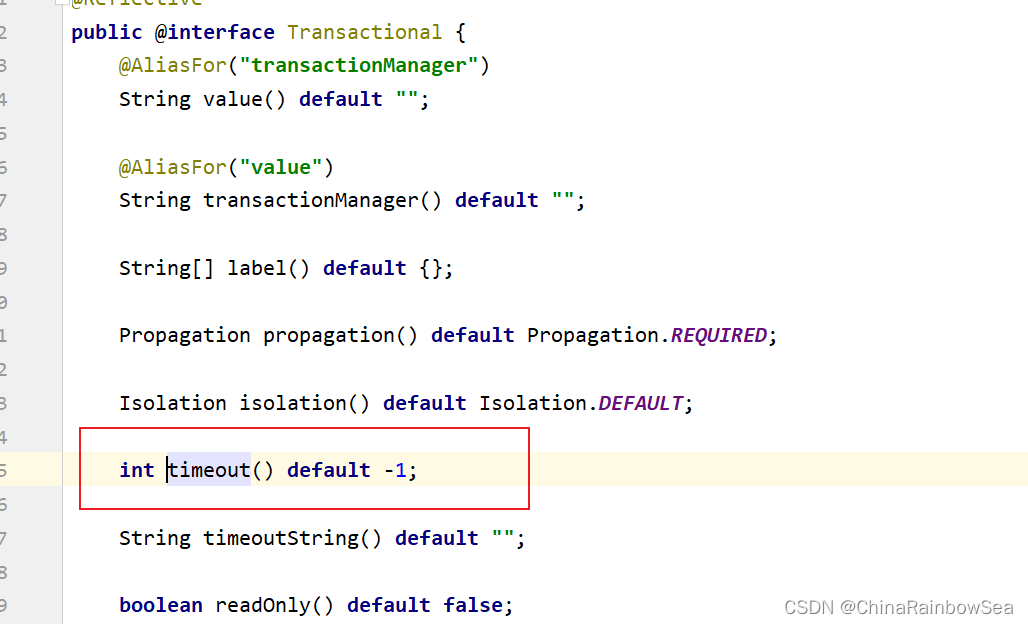
int timeout() default -1;
String timeoutString() default "";
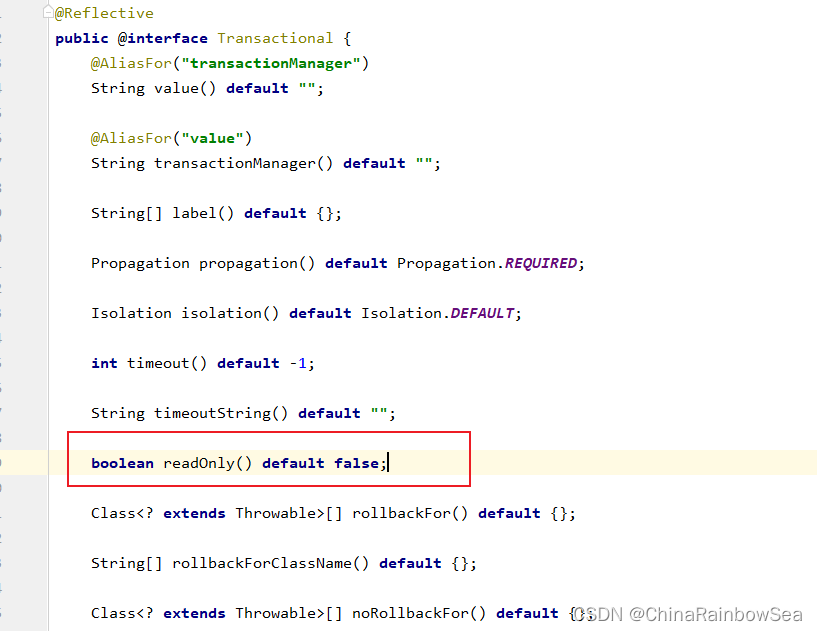
boolean readOnly() default false;
Class[] rollbackFor() default {};
String[] rollbackForClassName() default {};
Class[] noRollbackFor() default {};
String[] noRollbackForClassName() default {};
}
其中多个属性,我们需要更加关注如下几个重点属性:
- 事务的传播行为
- 事务的隔离级别
- 事务超时
- 只读事务
- 设置出现哪些异常回滚事务
- 设置出现哪些异常 不 回滚事务
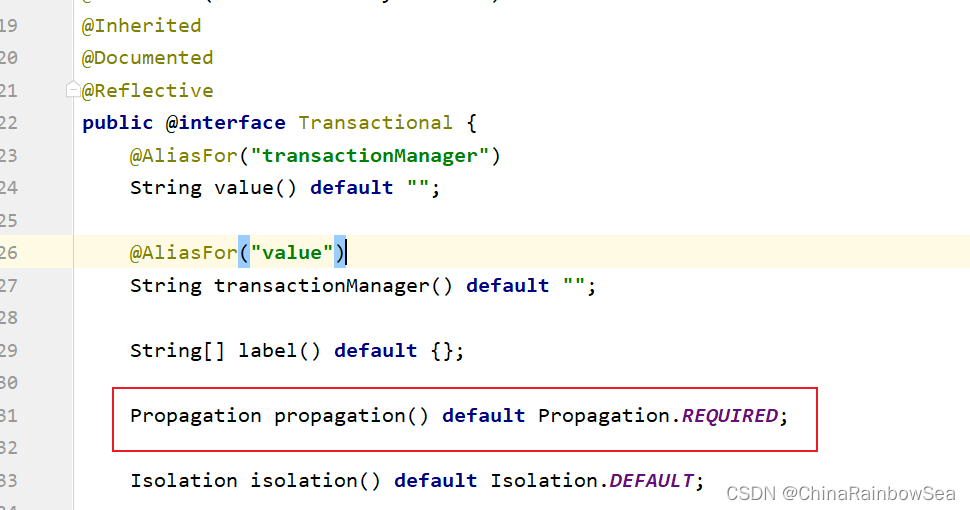
什么是事务的传播行为?
在Service 类中有 A( ) 方法和B( ) 方法,A( ) 方法上有事务,B( ) 方法上也有事务。
当A( ) 方法执行过程中调用了B( ) 方法,事务是如何传递的?
是统一合并为一个事务里, 还是开启一个新的事务?上述操作就是事务传播行为。
事务传播行为在Spring 框架中被定义为枚举类型:
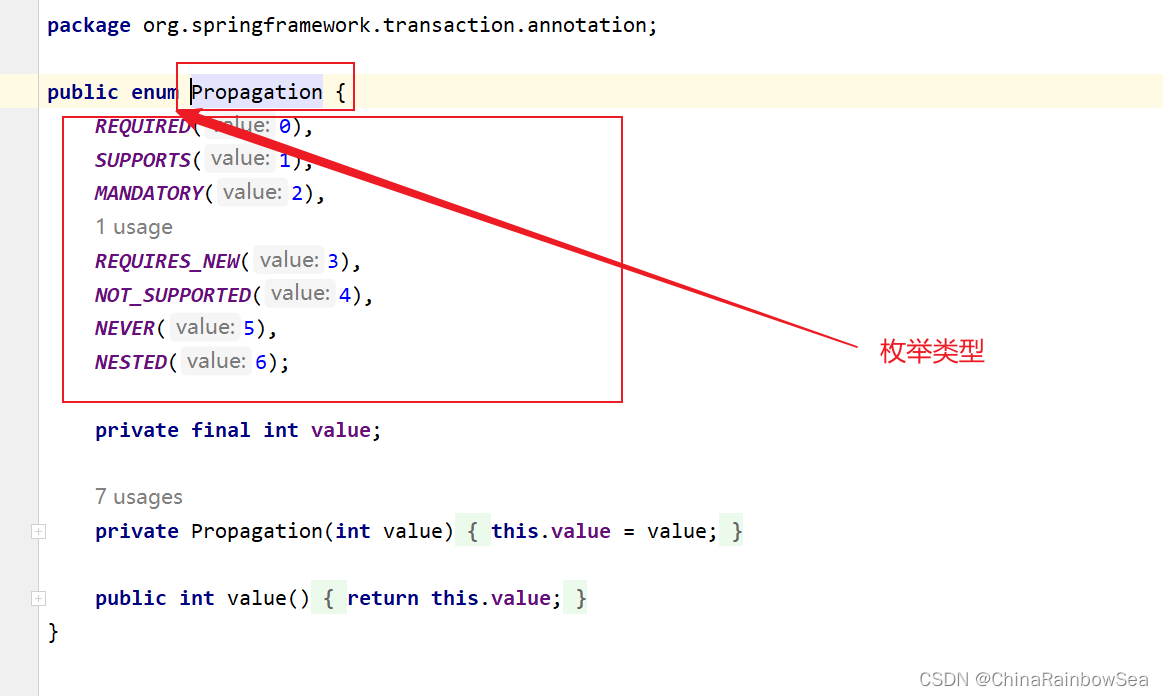
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.transaction.annotation;
public enum Propagation {
REQUIRED(0),
SUPPORTS(1),
MANDATORY(2),
REQUIRES_NEW(3),
NOT_SUPPORTED(4),
NEVER(5),
NESTED(6);
private final int value;
private Propagation(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int value() {
return this.value;
}
}
一共有七种传播行为:
- REQUIRED:支持当前事务,如果不存在就新建一个( 默认 ) 《没有事务就新建,有就加入事务,简单的说就是共用同一个事务处理》
- SUPPORTS:支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行 《有事务就加入,没有就不管了》
- MANDATORY:必须运行在一个事务中,如果当前没有事务正在发生,将抛出一个异常 《有事务就加入事务,没有就抛异常》
- REQUIRES_NEW:开启一个新的事务,如果一个事务已经存在,则将这个存在的事务挂起。 《不管有没有,直接开启一个新事务,开启的事务和之前的事务不存在嵌套关系,之前的事务被挂起,简单的说,就是不会共用一个事务,而是各自不同的DML生成不同的事务》
- NOT_SUPPORTED:以非事务方式运行,如果有事务存在,挂起事务 《不支持事务,存在就挂起事务》
- NEVER:以非事务的方式运行,如果有事务存在,抛出异常 《不支持事务,存在就抛异常》
- NESTED:如果当前正有一个事务在进行中,则该方法应当运行在一个嵌套式事务当中,被嵌套的事务可以独立于外层事务,进行提交或回滚。如果外层事务不存在,行为就像REQUIRED一样。 《有事务的话,就在这个事务里,再嵌套一个完全独立的事务,嵌套的事务可以独立的提交和独立的回滚。没有事务就和 REQUIRED 一样处理》
为了更好的直观的观察事务的传播行为,这里我们引入: 集成Log4j2日志框架,在日志信息中可以看到更加详细的信息。
首先在
pom.xml
配置文件当中引入 Log4j2 日志框架的相关依赖
org.apache.logging.log4j
log4j-core
2.19.0
org.apache.logging.log4j
log4j-slf4j2-impl
2.19.0
完整的
pom.xml
配置文件信息
4.0.0
org.example
spring6-013-tx-bank
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
17
17
repository.spring.milestone
Spring Milestone Repository
https://repo.spring.io/milestone
org.springframework
spring-context
6.0.11
org.springframework
spring-aop
6.0.11
org.springframework
spring-jdbc
6.0.11
org.springframework
spring-aspects
6.0.11
mysql
mysql-connector-java
8.0.30
com.alibaba
druid
1.2.13
jakarta.annotation
jakarta.annotation-api
2.1.1
junit
junit
4.13.2
test
org.apache.logging.log4j
log4j-core
2.19.0
org.apache.logging.log4j
log4j-slf4j2-impl
2.19.0
在导入配置 Log4j2 的 资源上的配置,
xml
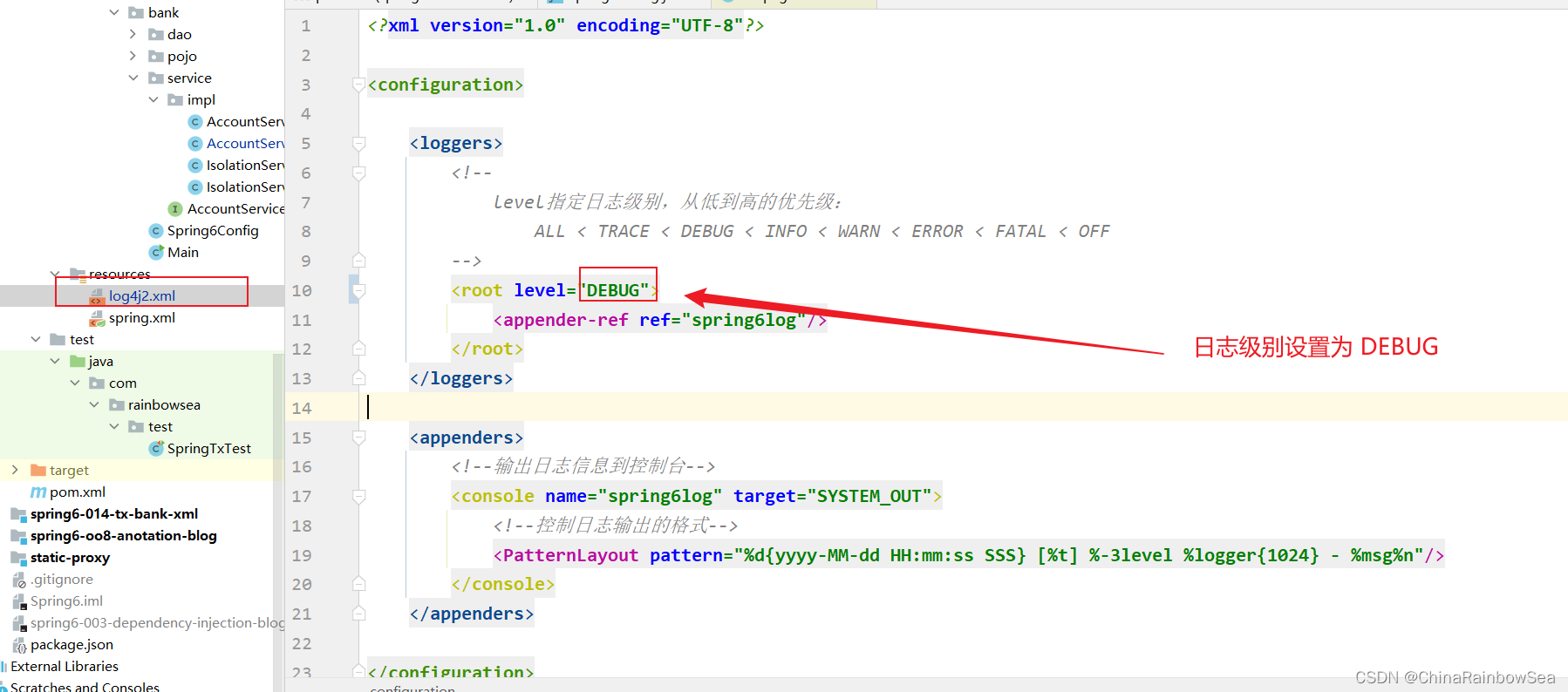
在代码中设置事务的传播行为:
这里,我们测试:REQUIRED:支持当前事务,如果不存在就新建一个( 默认 ) 《没有事务就新建,有就加入事务,简单的说就是共用同一个事务处理》
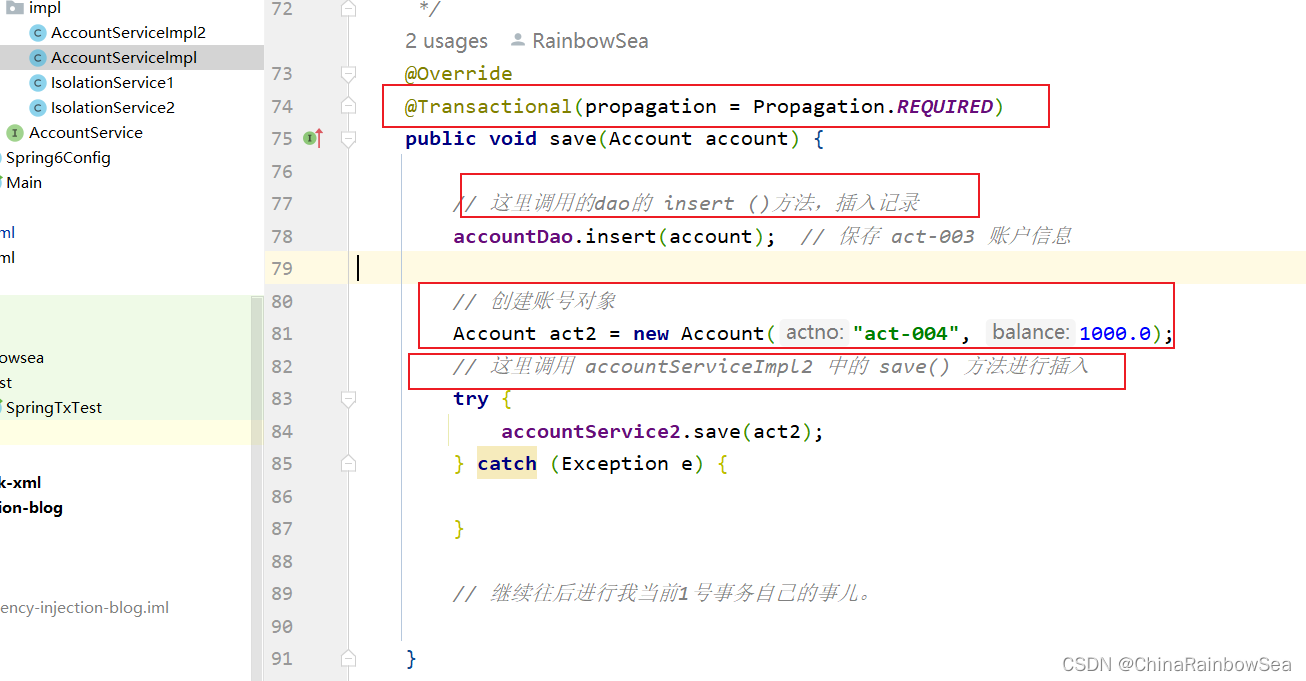
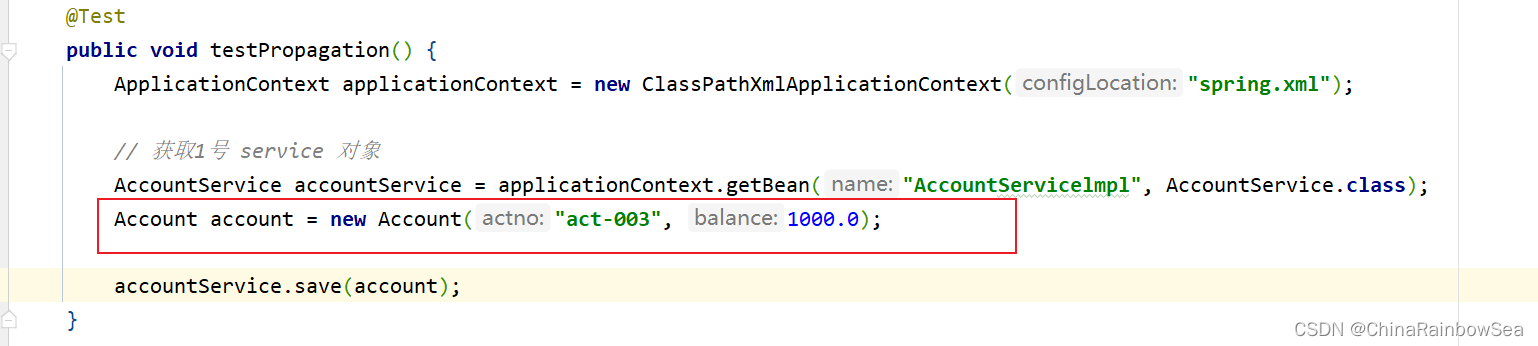
这里我们测试,在 AccountServicelmpl 类当中的 save() 方法创建一个新的账户“"act-003", 1000.0”,然后在 AccountServicelmpl 类的 save() 方法当中,调用 AccountServicelmpl2类当中的 save( ) 方法,添加 "act-004", 1000.0 新的账户信息。
我们这里添加两个新的账户,一个是“act-003" 是 在AccountServicelmpl 类当中的 save() 方法 保存的,而另一个则是“act-004”账户是在,AccountServicelmpl 2 类当中的 save() 方法保存的,同时在这个AccountServicelmpl2 类当中的 save() 方法,添加上异常,导致添加账户失败,按照
我们的REQUIRED:支持当前事务,如果不存在就新建一个( 默认 ) 《没有事务就新建,有就加入事务,简单的说就是共用同一个事务处理》 的特点,该两个添加账户的操作,归属于同一个事务,其中一个添加账户信息失败了,就全部失败。事务发生回滚操作。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.service.AccountService;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Component(value = "AccountServicelmpl")
public class AccountServicelmpl implements AccountService {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl") // @Resource 根据名称进行set 注入赋值
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Resource(name = "accountServiceImpl2")
private AccountService accountService2;
/**
* 保护账号信息
*
* @param account
*/
@Override
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void save(Account account) {
// 这里调用的dao的 insert ()方法,插入记录
accountDao.insert(account); // 保存 act-003 账户信息
// 创建账号对象
Account act2 = new Account("act-004", 1000.0);
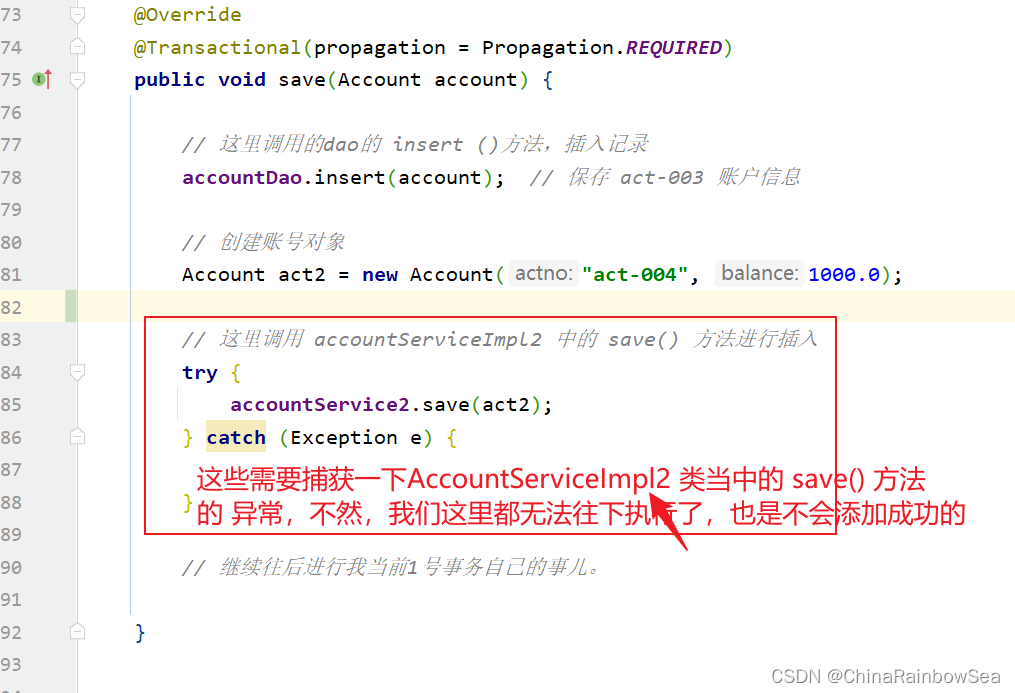
// 这里调用 accountServiceImpl2 中的 save() 方法进行插入
try {
accountService2.save(act2);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
// 继续往后进行我当前1号事务自己的事儿。
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.service.AccountService;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service(value = "accountServiceImpl2") // 给Spring 管理起来
public class AccountServiceImpl2 implements AccountService {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl") // accountDaoImpl 已经交给Spring 管理,所以这里可以直接用 @Resource 根据名称set注入
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void save(Account account) {
accountDao.insert(account);
//模拟异常
String s = null;
s.toString();
// 事儿没有处理完,这个大括号当中的后续也许还有其他的DML语句。
}
}
运行测试;
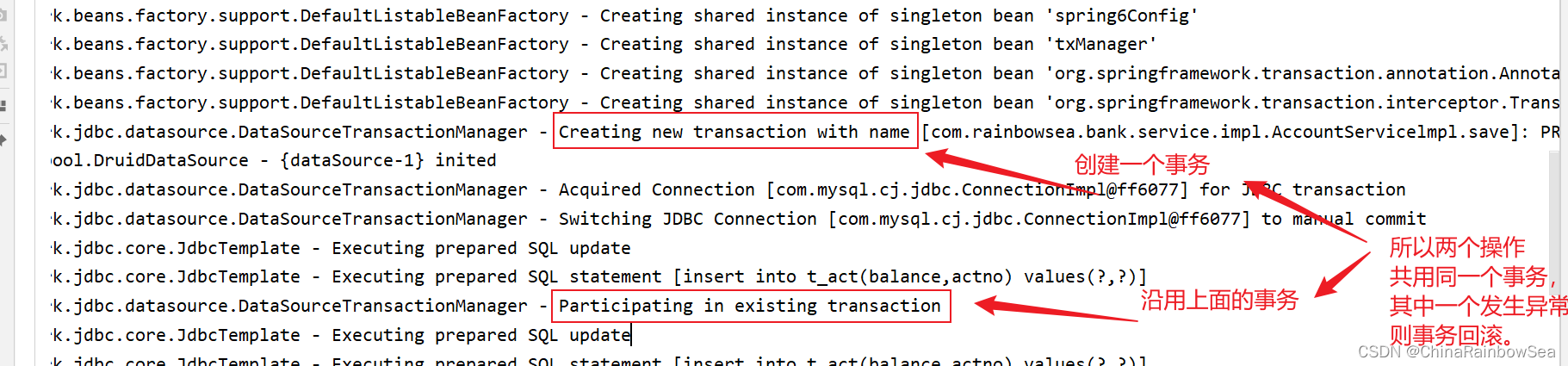
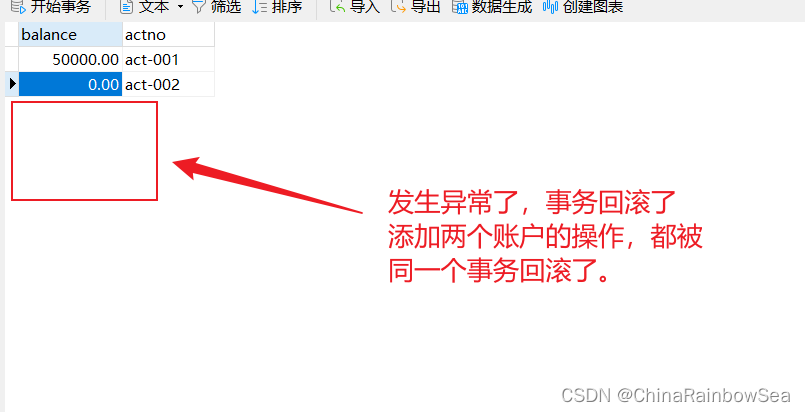
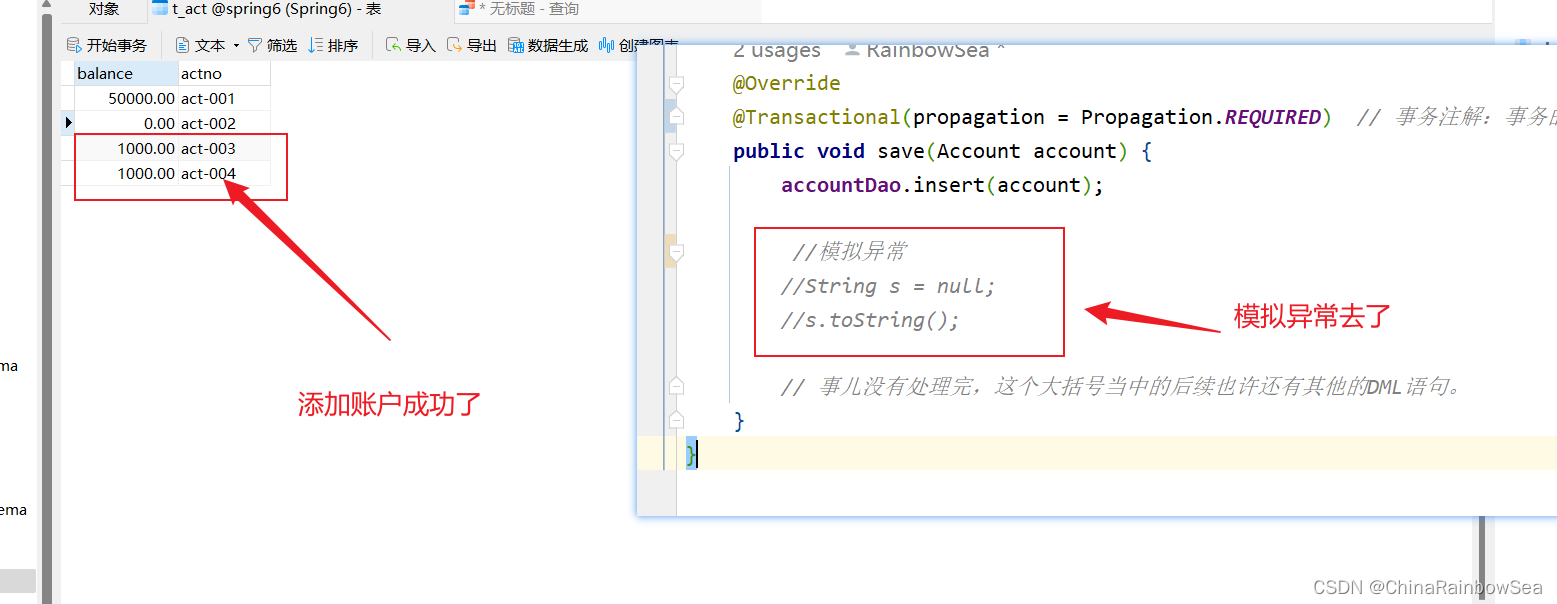
这里我们再关闭异常,看看是否添加成功。
下面我们再测试一个:REQUIRES_NEW:开启一个新的事务,如果一个事务已经存在,则将这个存在的事务挂起。 《不管有没有,直接开启一个新事务,开启的事务和之前的事务不存在嵌套关系,之前的事务被挂起,简单的说,就是不会共用一个事务,而是各自不同的DML生成不同的事务》 的传播行为。各自用各自的事务。
这里我们把添加的账户信息删除一下,方便后续的操作。
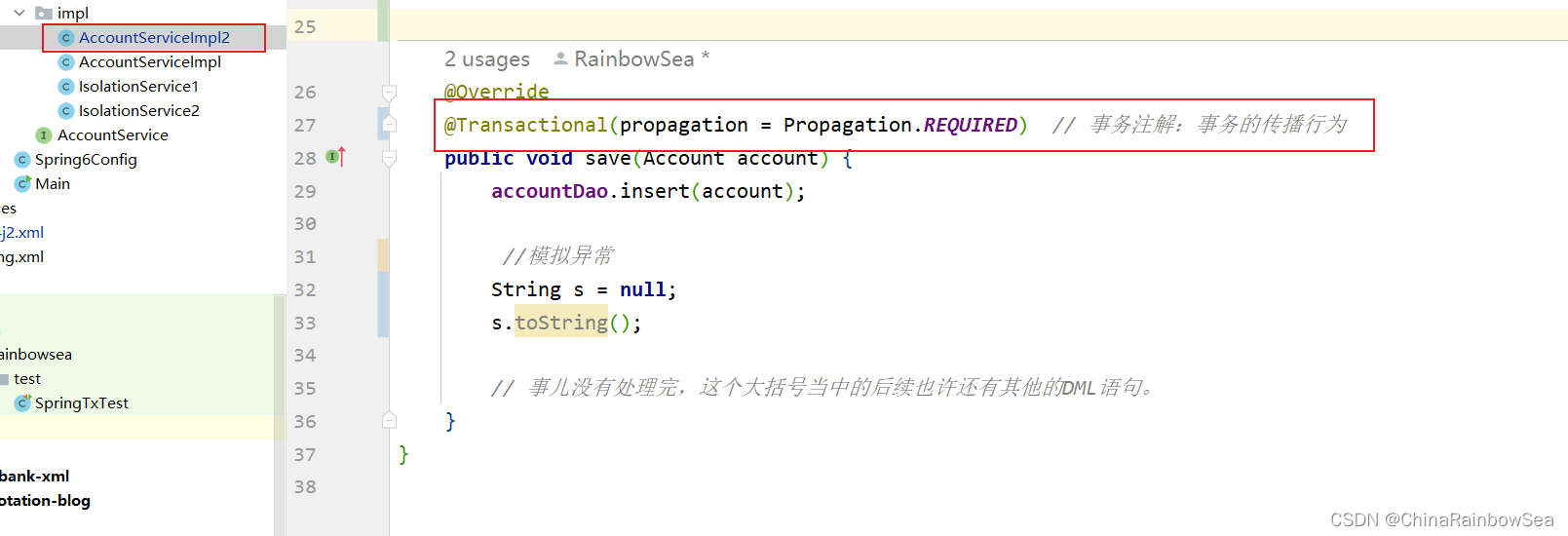
下面我们将 AccountServicelmpl2 类当中的 save() 方法 上的事务传播行为设置为:REQUIRES_NEW 进行测试,再次测试添加两个账户信息的操作。
同样开启对 AccountServicelmpl 2 类当中的 save() 方法,添加上异常。
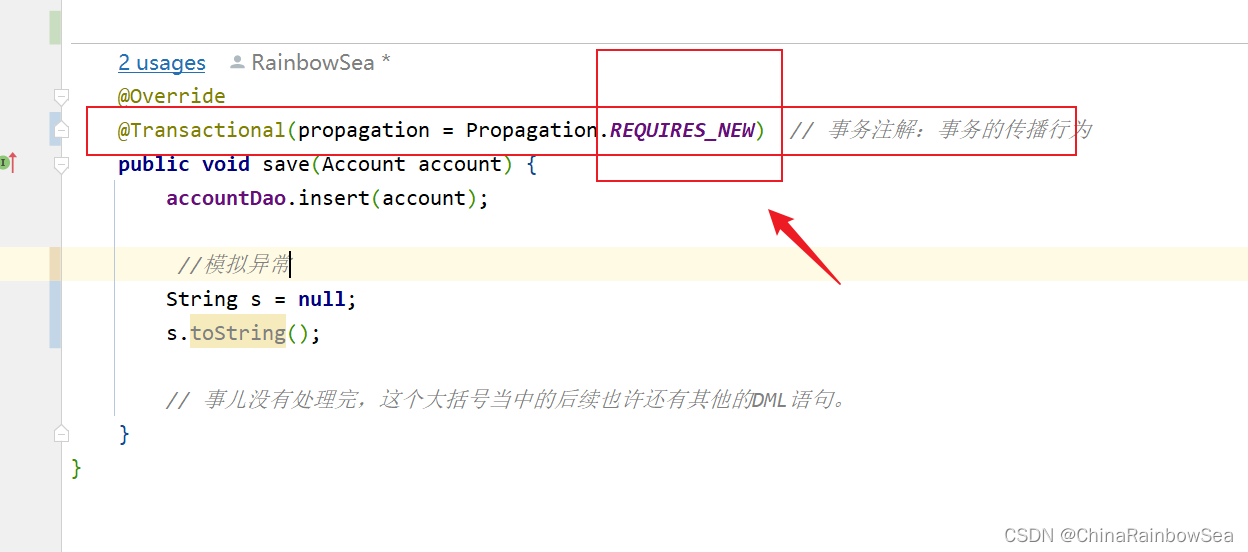
@Override
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW) // 事务注解:事务的传播行为
public void save(Account account) {
accountDao.insert(account);
//模拟异常
String s = null;
s.toString();
// 事儿没有处理完,这个大括号当中的后续也许还有其他的DML语句。
}
}
运行测试:
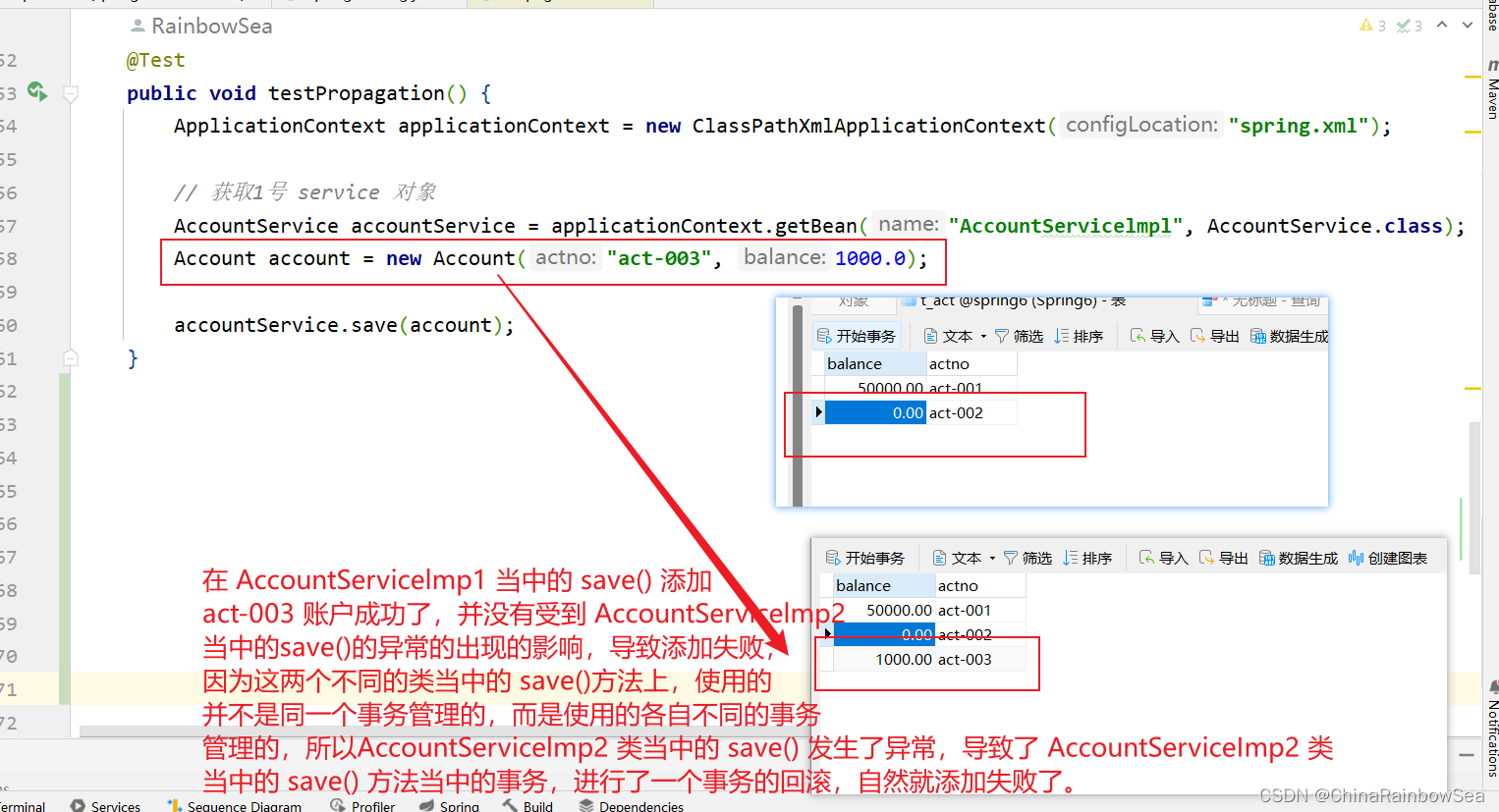
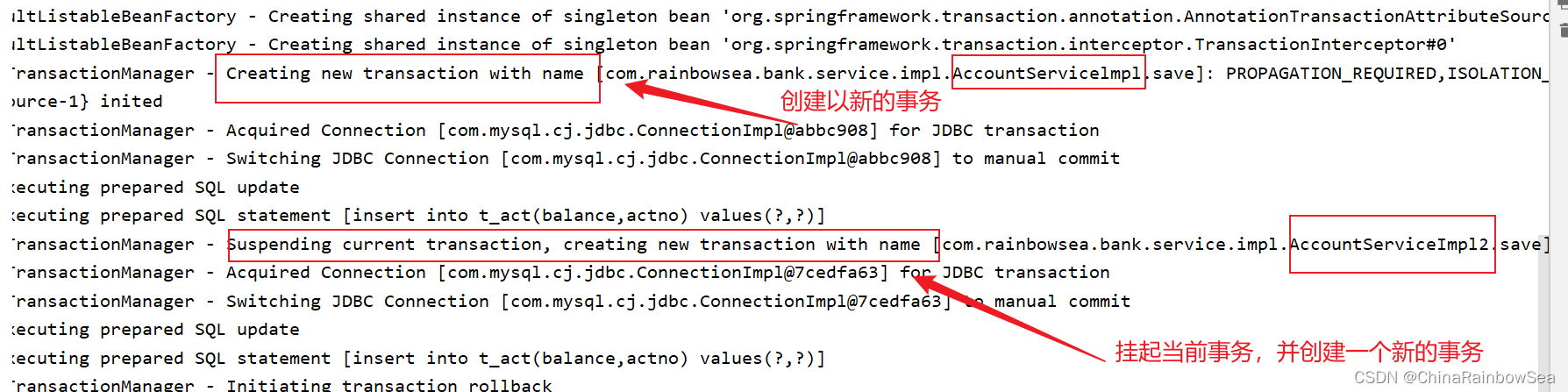
各自使用的是各自的事务进行了控制,不是同一个事务进行控制的 。
在 AccountServicelmp1 当中的 save() 添加
act-003 账户成功了,并没有受到 AccountServicelmp2
当中的save()的异常的出现的影响,导致添加失败,
因为这两个不同的类当中的 save()方法上,使用的
并不是同一个事务管理的,而是使用的各自不同的事务
管理的,所以AccountServicelmp2 类当中的 save() 发生了异常,导致了 AccountServiceImp2 类
当中的 save() 方法当中的事务,进行了一个事务的回滚,自然就添加失败了。
事务的隔离级别类似于教室A和教室B之间的那道墙,隔离级别越高表示墙体越厚,隔音效果越好。数据库中读取数据存在的三大问题:
- 脏读:读取到没有提交的数据库的数据,叫做脏读
- 不可重复读:在同一个事务当中,第一次和第二次读取的数据不一样。(并发,多线程就会涉及的不可重复读)
- 幻读:读到的数据是假的
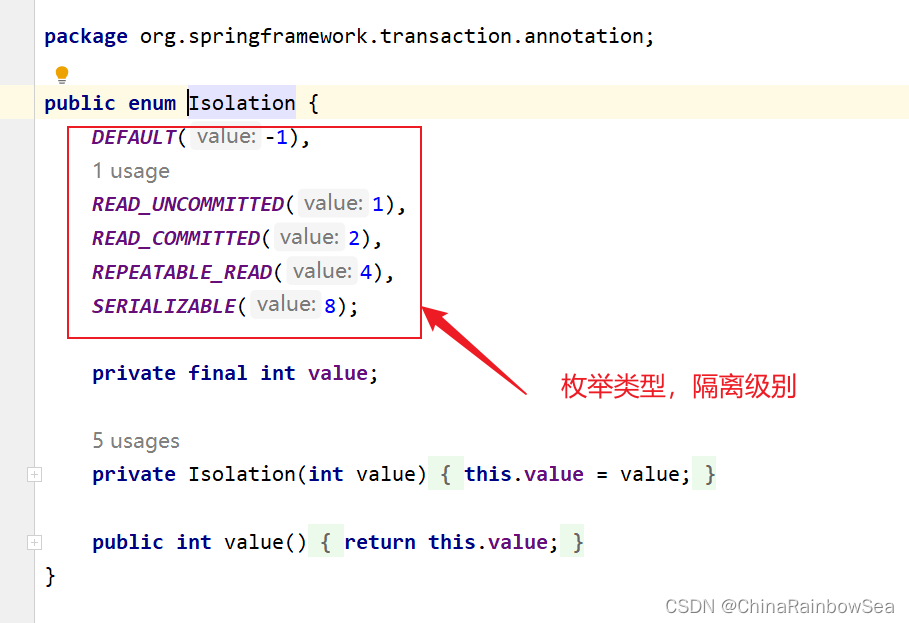
事务的隔离级别包括四个级别:
读未提交:READ_UNCOMMITTED
- 这种隔离级别,存在脏读问题,所谓的脏读(dirty read)表示能够读取到其它事务未提交的数据。
读提交:READ_COMMITTED
- 解决了脏读问题,其它事务提交之后才能读到,但存在不可重复读问题(Oracel 默认)
可重复读:REPEATABLE_READ
- 解决了不可重复度,可以达到可重复读效果,只要当前事务不结束,读取到的数据一直都是一样的。但存在 幻读 问题。 MySQL默认 是个隔离级别
序列化:SERIALIZABLE
- 解决了幻读问题,事务排序执行。但不支持并发。
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 读未提交 | 有 | 有 | 有 |
| 读提交 | 无 | 有 | 有 |
| 可重复读 | 无 | 无 | 有 |
| 序列化 | 无 | 无 | 无 |
在Spring框架中隔离级别在spring中以枚举类型存在:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.transaction.annotation;
public enum Isolation {
DEFAULT(-1),
READ_UNCOMMITTED(1),
READ_COMMITTED(2),
REPEATABLE_READ(4),
SERIALIZABLE(8);
private final int value;
private Isolation(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int value() {
return this.value;
}
}
在Spring 当中事务的隔离级别上的设置,使用注解:
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)
这里我们测试:事务隔离级别:READ_UNCOMMITTED 和 READ_COMMITTED
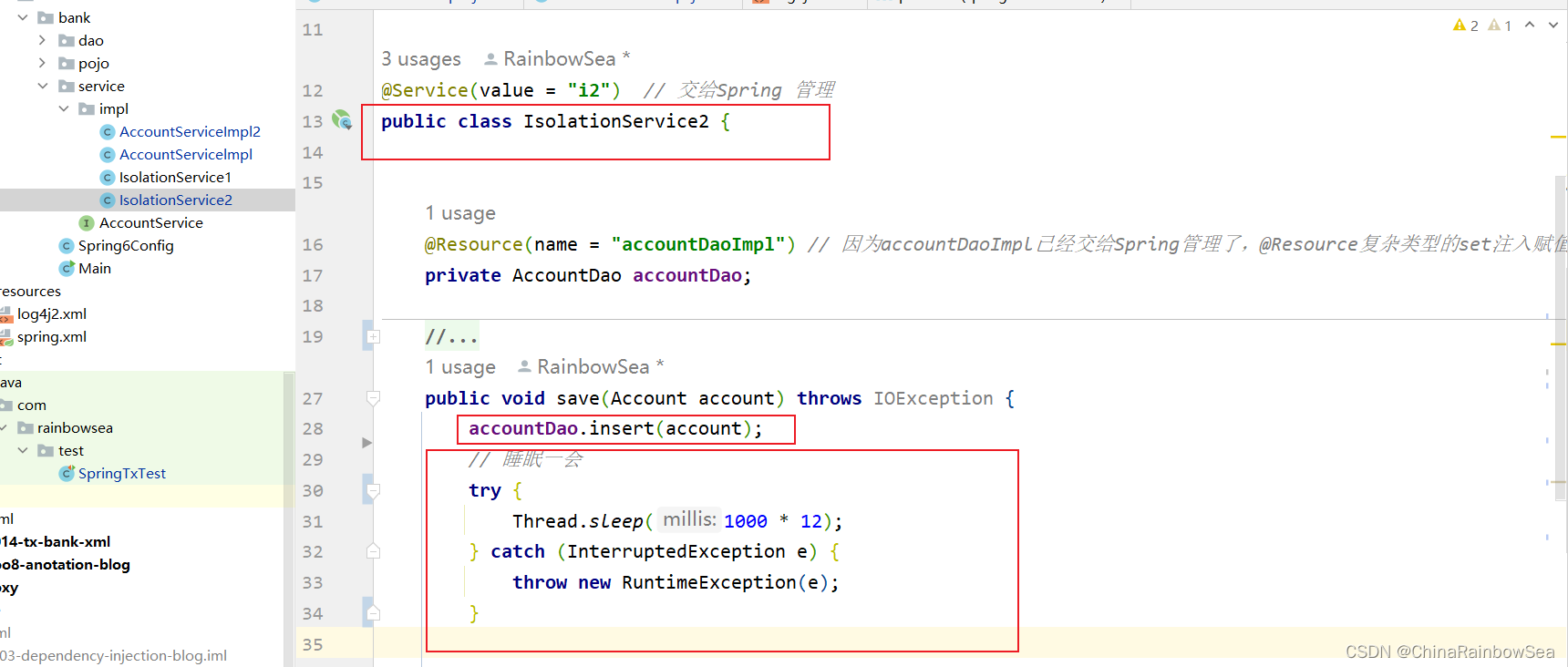
怎么测试:一个service负责插入,一个service负责查询。负责插入的service要模拟延迟。
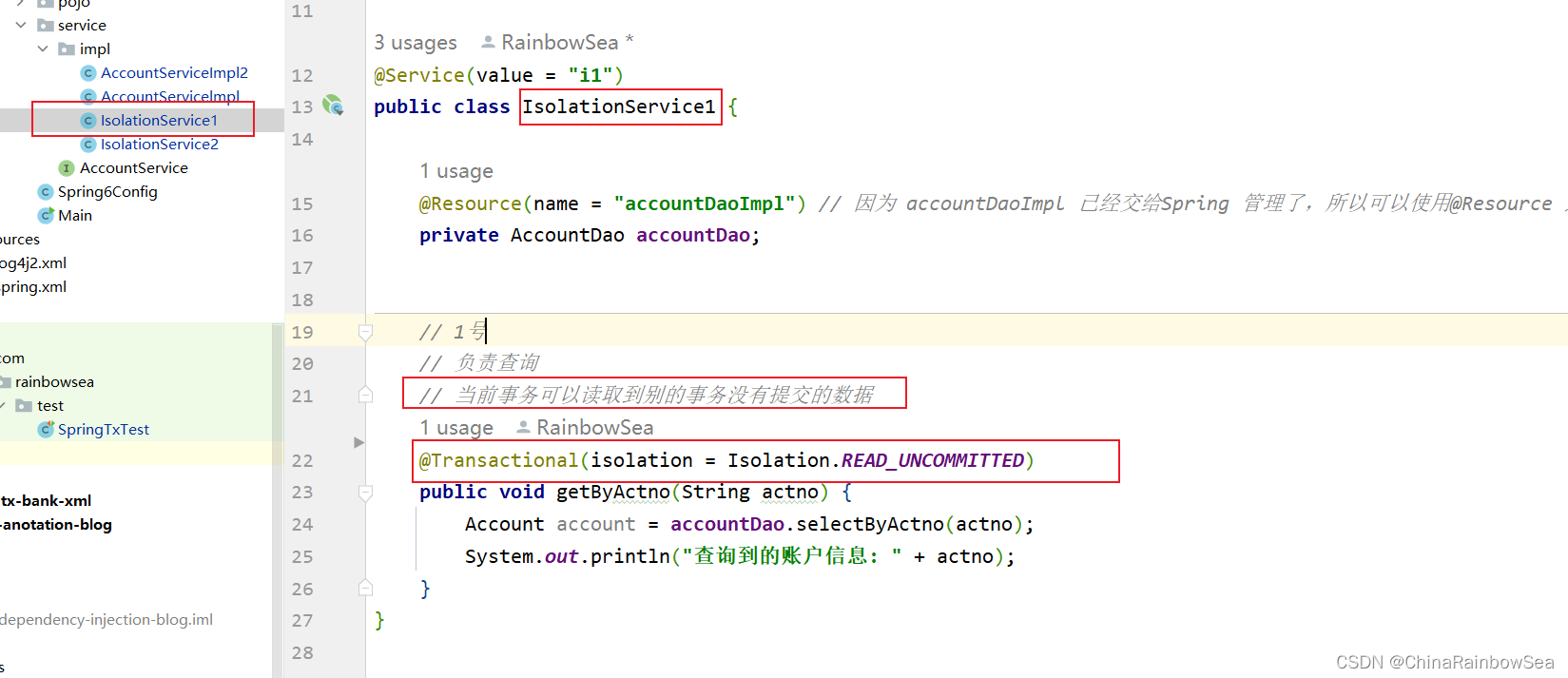
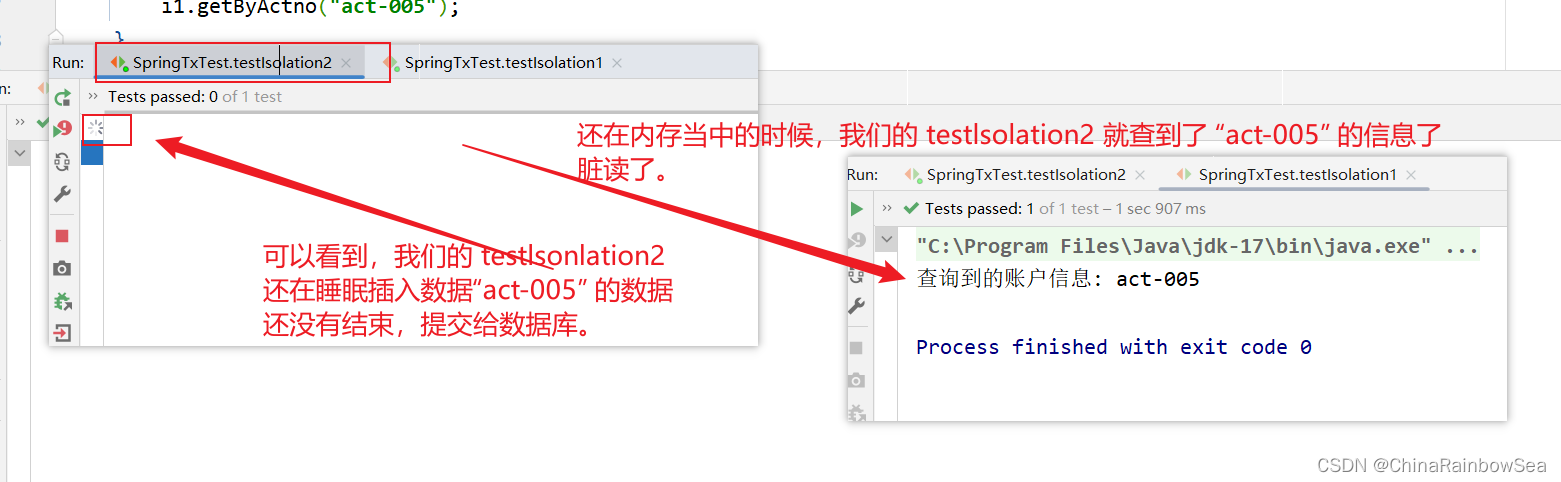
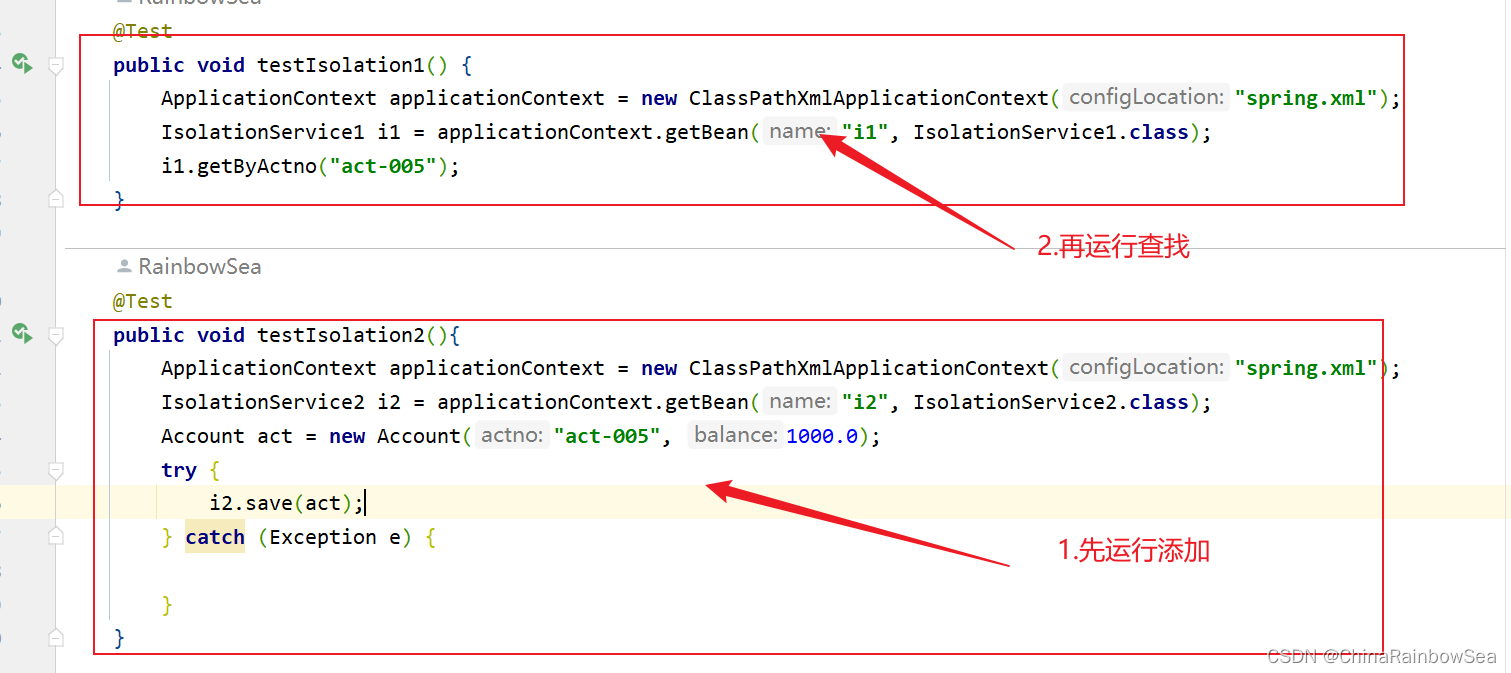
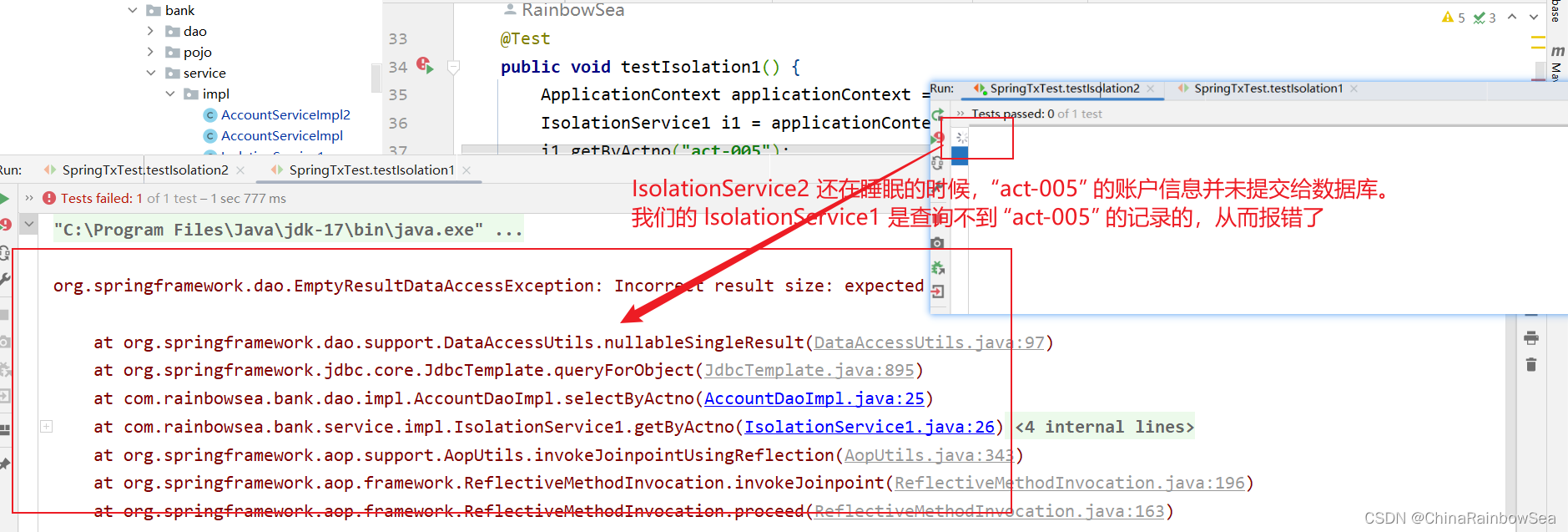
IsolationService2 类 save()方法负责,插入一个账户信息 ”act-005“,同时睡眠12秒中,当其还在睡眠当中时(没有提交给数据库,而是在内存当中)的时候,我们的IsolationService1 getByActno( ) 方法根据其插入的“act-005” 账户去查,这时候的 act-005 还在内存当中,我们并没有提交给数据库,看看能否查到?
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.io.IOException;
@Service(value = "i2") // 交给Spring 管理
public class IsolationService2 {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl") // 因为accountDaoImpl已经交给Spring管理了,@Resource复杂类型的set注入赋值
private AccountDao accountDao;
// 2号
//负责insert
public void save(Account account) throws IOException {
accountDao.insert(account);
// 睡眠一会
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 * 12);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service(value = "i1")
public class IsolationService1 {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl") // 因为 accountDaoImpl 已经交给Spring 管理了,所以可以使用@Resource 进行非简单类型的赋值
private AccountDao accountDao;
// 1号
// 负责查询
// 当前事务可以读取到别的事务没有提交的数据
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITTED)
public void getByActno(String actno) {
Account account = accountDao.selectByActno(actno);
System.out.println("查询到的账户信息: " + actno);
}
}
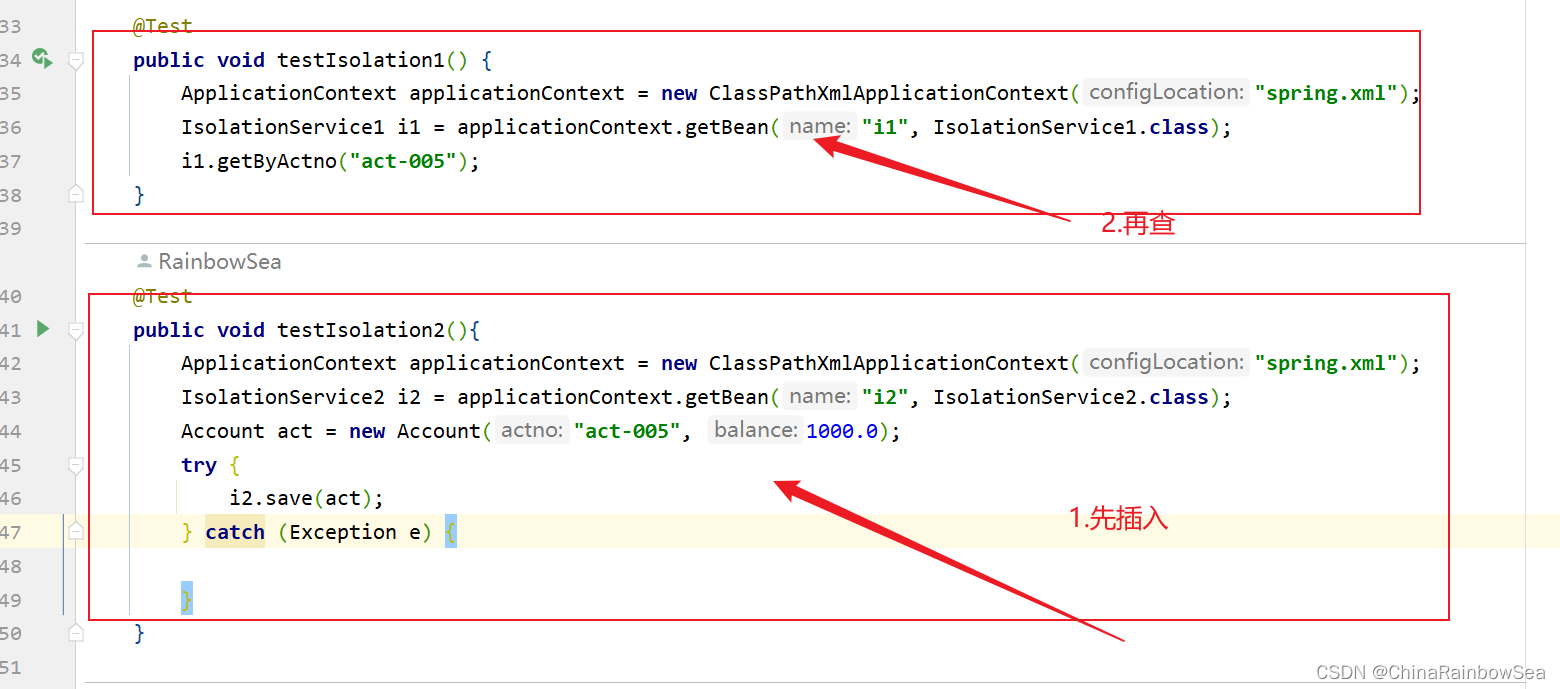
@Test
public void testIsolation1() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
IsolationService1 i1 = applicationContext.getBean("i1", IsolationService1.class);
i1.getByActno("act-005");
}
@Test
public void testIsolation2(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
IsolationService2 i2 = applicationContext.getBean("i2", IsolationService2.class);
Account act = new Account("act-005", 1000.0);
try {
i2.save(act);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
运行结果:
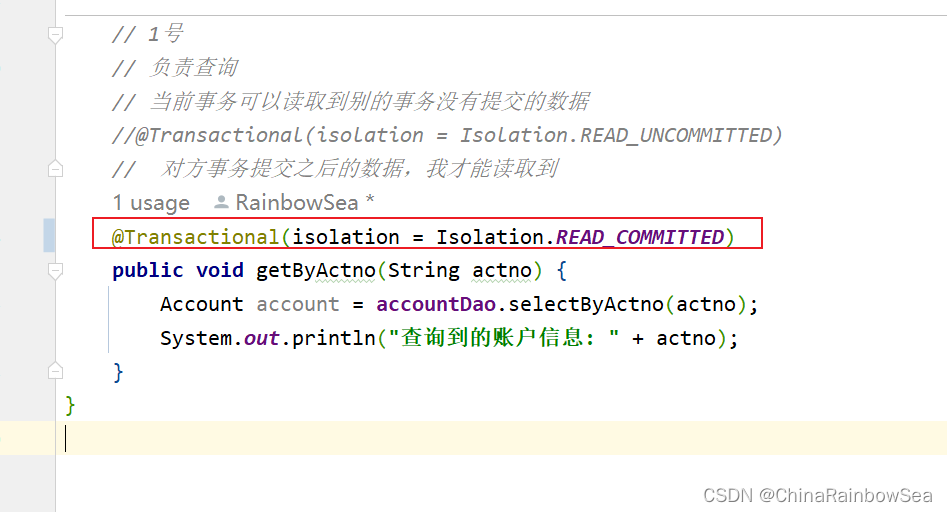
下面我们将:其设置为:READ_COMMITTED,就无法脏读了(无法读取到内存当中的信息),只有当对方:对方事务提交之后的数据,我才能读取到。
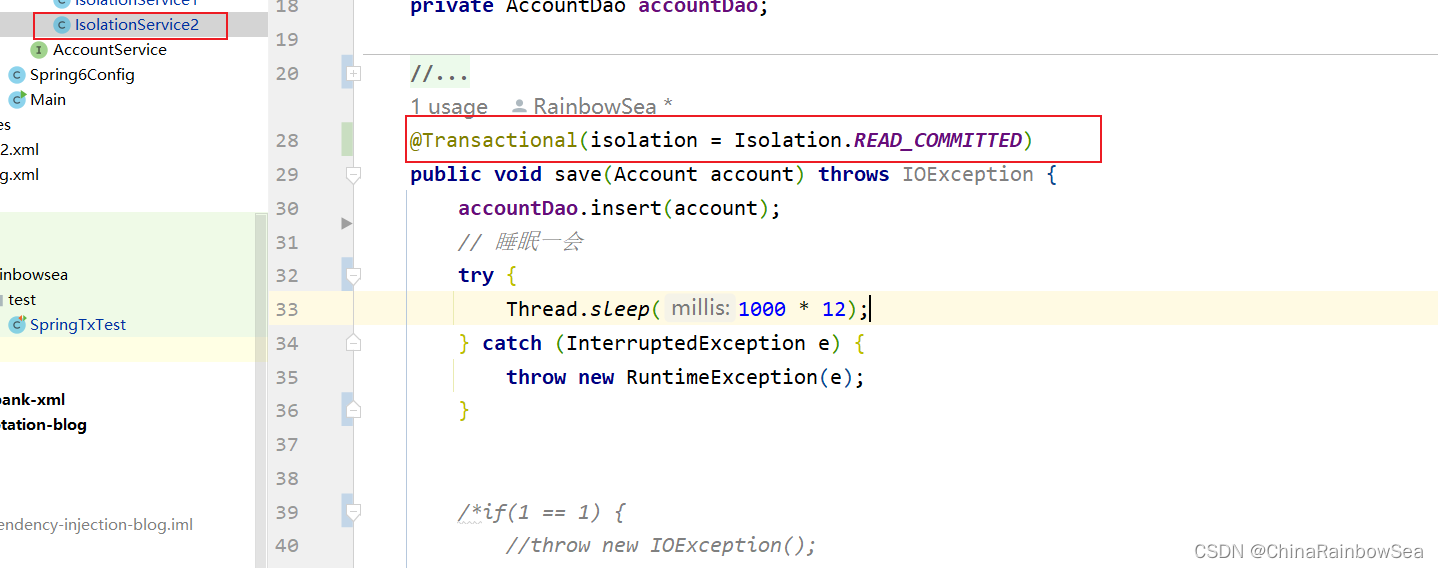
我们的IsolationService2 也要设置为:READ_COMMITTED,就无法脏读了(无法读取到内存当中的信息),只有当对方:对方事务提交之后的数据,我才能读取到。
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.io.IOException;
@Service(value = "i2") // 交给Spring 管理
public class IsolationService2 {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl") // 因为accountDaoImpl已经交给Spring管理了,@Resource复杂类型的set注入赋值
private AccountDao accountDao;
// 2号
//负责insert
// 或者整个异常的子类异常,都不回滚,其他异常回滚
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)
public void save(Account account) throws IOException {
accountDao.insert(account);
// 睡眠一会
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 * 12);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}。
}
}
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Service(value = "i1")
public class IsolationService1 {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl") // 因为 accountDaoImpl 已经交给Spring 管理了,所以可以使用@Resource 进行非简单类型的赋值
private AccountDao accountDao;
// 1号
// 负责查询
// 当前事务可以读取到别的事务没有提交的数据
//@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_UNCOMMITTED)
// 对方事务提交之后的数据,我才能读取到
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED)
public void getByActno(String actno) {
Account account = accountDao.selectByActno(actno);
System.out.println("查询到的账户信息: " + actno);
}
}
同样我们还是:插入 “act-005” 的账户信息,进行测试,看看还能不能查询到结果了。
通过执行结果可以清晰的看出隔离级别不同,执行效果不同。
在Spring框架的 @Transactional 注解 当中可以设置事务的超时时间:
@Transactional(timeout = 10)
// 表示设置事务的超时时间为:10秒
表示超过10秒如果该事务中所有的 DML语句还没有执行完毕的话,最终结果会选择回滚。
默认值为 -1;表示没有时间限制。
注意这里有个坑,事务的超时时间指的是哪段时间?
在当前事务当中,最后一条DML语句执行之前的时间。如果最后一条DML语句后面很多很多业务逻辑,这些业务代码执行的时间是不被计入超时时间。
如下测试:
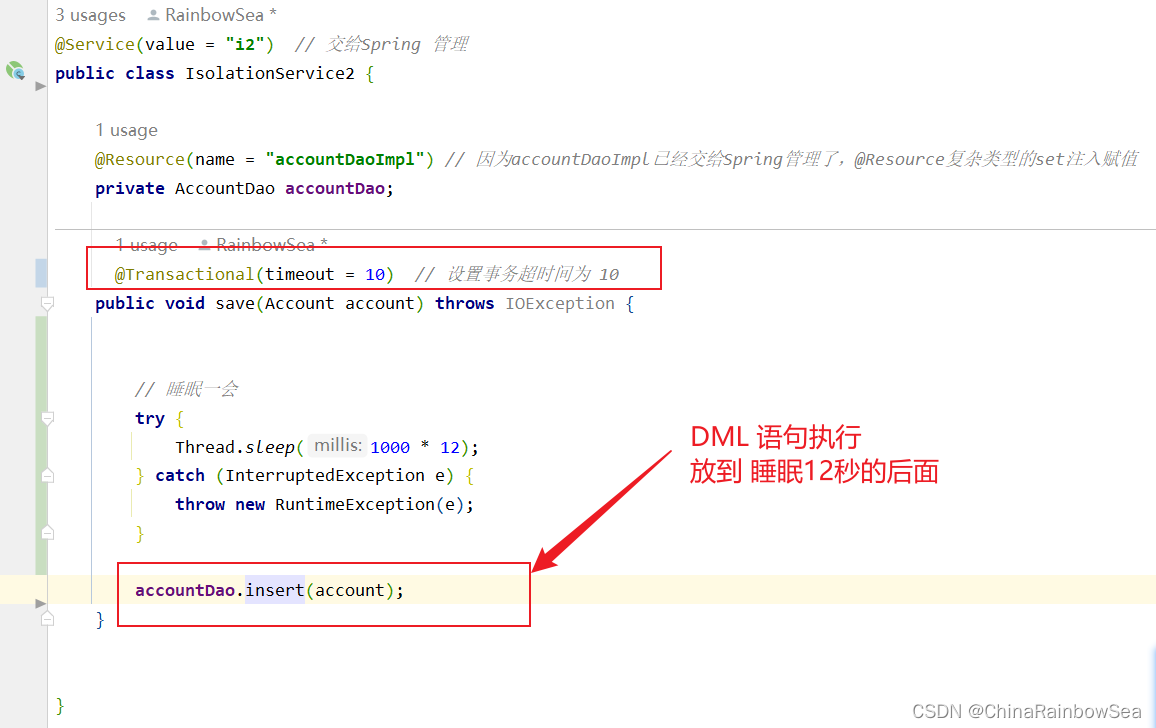
我们首先将 DML 语句放在 睡眠 12 秒之前,看看后面的业务处理时间,是否会被记录到超时时间内,会(则超时了,事务会发生回滚);不会(则没有超时,不计入后面的时间,事务不发生回滚)
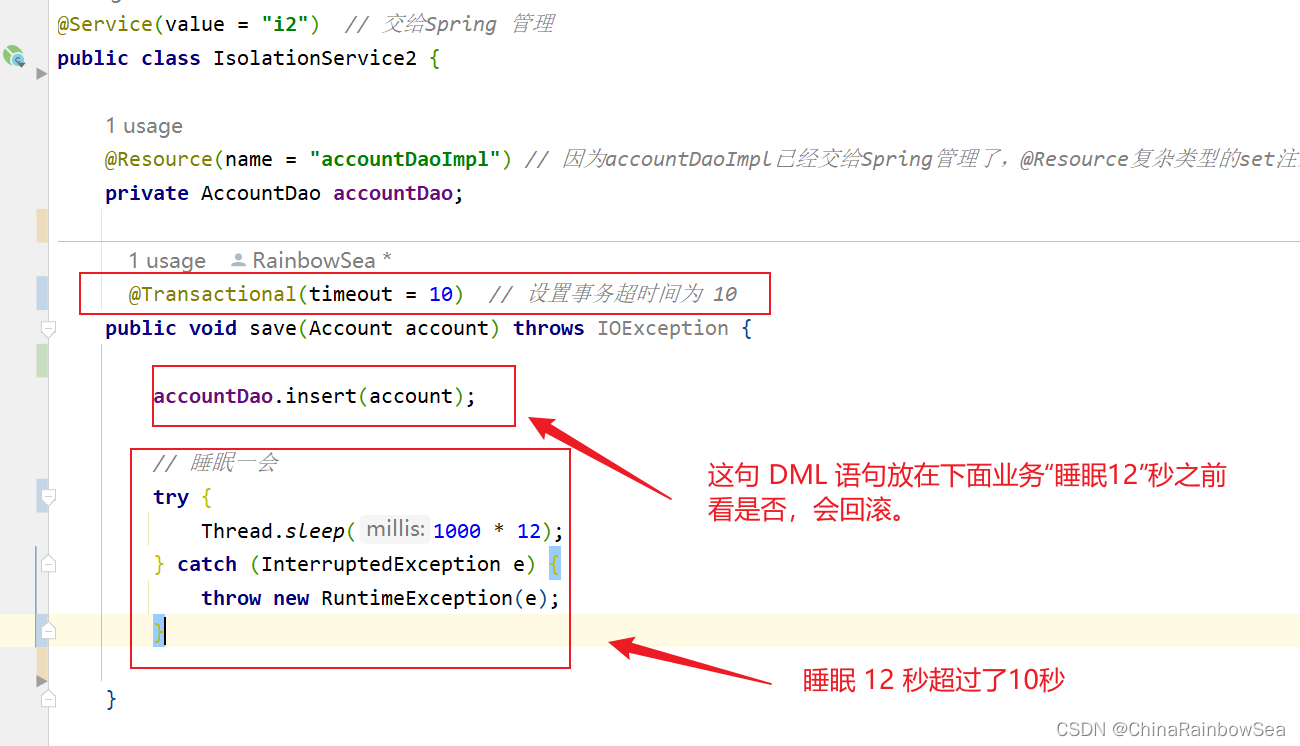
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.io.IOException;
@Service(value = "i2") // 交给Spring 管理
public class IsolationService2 {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl") // 因为accountDaoImpl已经交给Spring管理了,@Resource复杂类型的set注入赋值
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Transactional(timeout = 10) // 设置事务超时间为 10
public void save(Account account) throws IOException {
accountDao.insert(account);
// 睡眠一会
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 * 12);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
下面我们重新将该添加的“act-003” 的数据删除了。
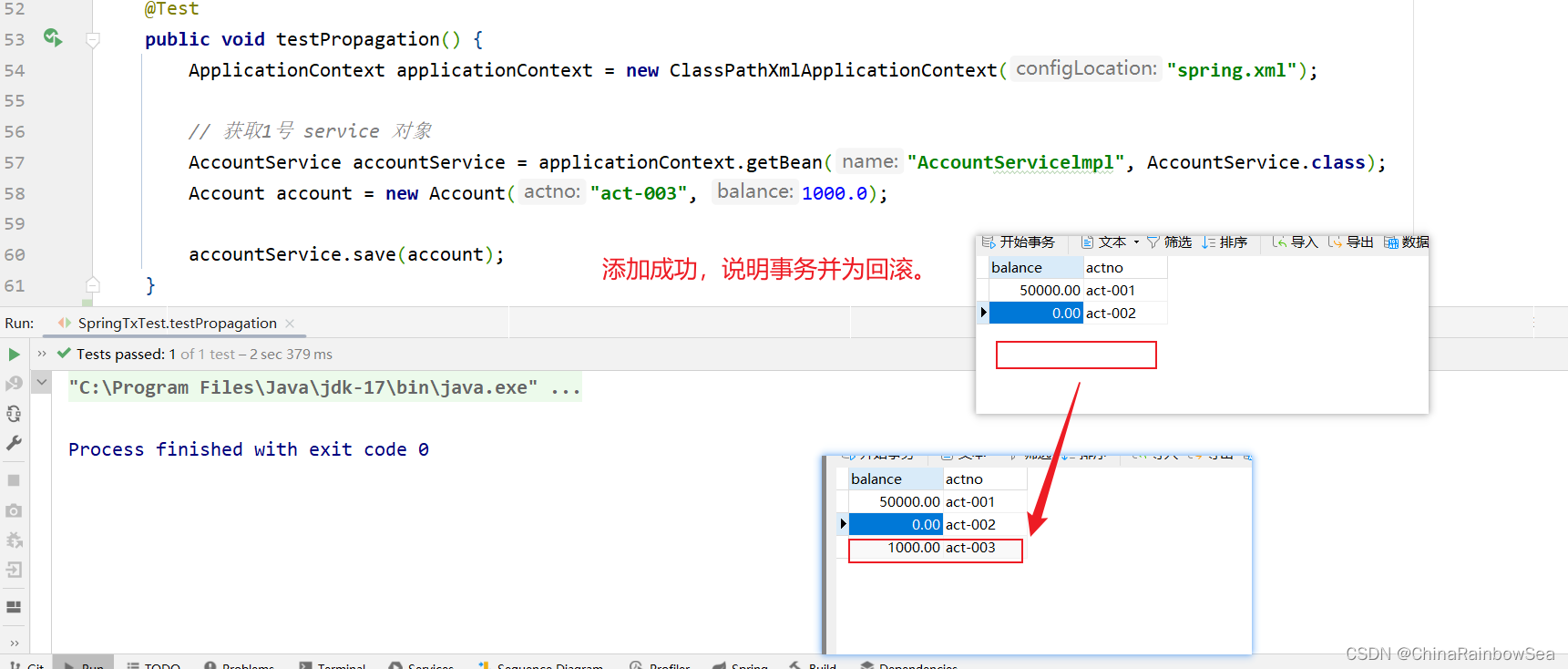
这次我们将 DML 语句放到 “睡眠 12秒”的最后面,看看事务是否会发生回滚
运行
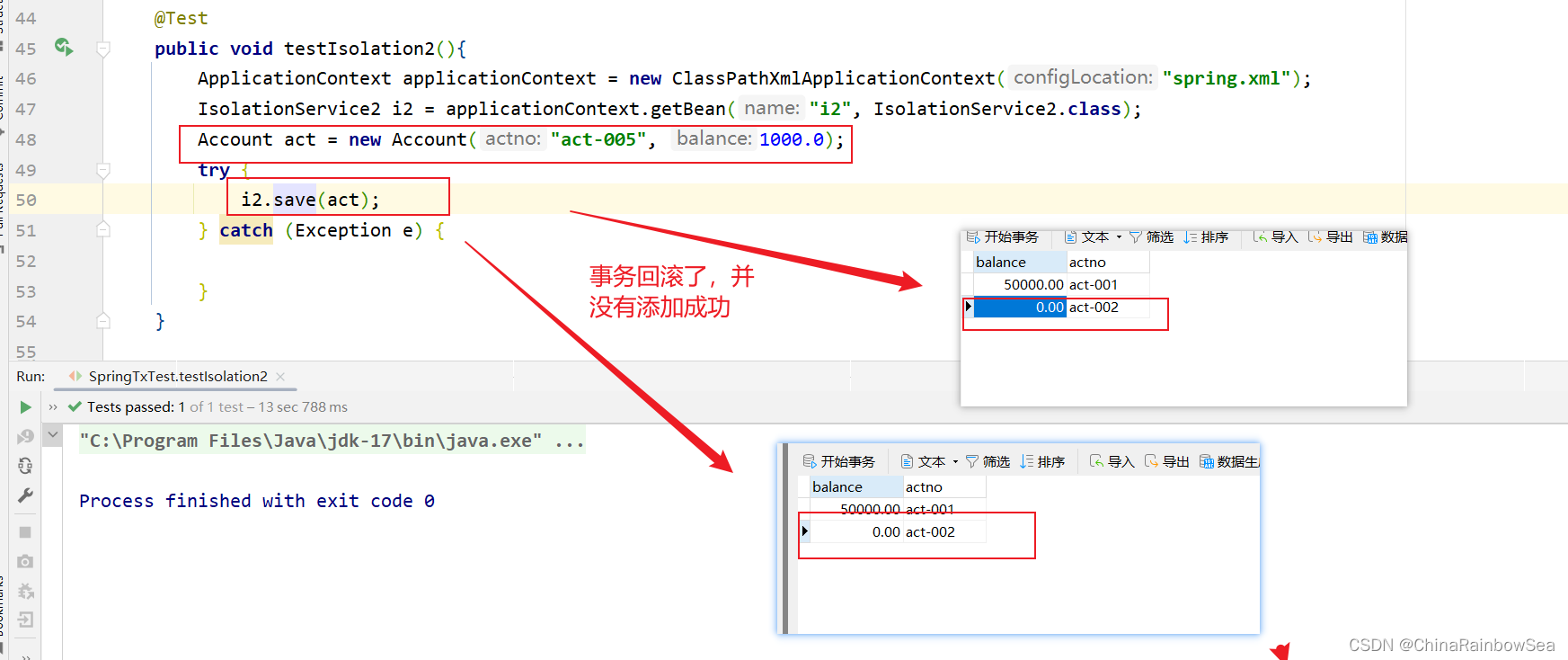
@Test
public void testIsolation2(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
IsolationService2 i2 = applicationContext.getBean("i2", IsolationService2.class);
Account act = new Account("act-005", 1000.0);
try {
i2.save(act);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
当然,如果想让整个方法的所有代码都计入超时时间的话,可以在方法最后一行添加一行无关紧要的DML语句(比如:判断语句之类的)。
如果像让当前事务设置为:只读事务可以用如下代码注解。
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
在该事务执行过程中只能读(只允许 select 语句执行“查”),delete , insert, update 均不可执行。
该特性的作用是: 启动Spring 框架的优化策略,提高 select 语句执行效率 。
如果该事务中确实没有增删改操作,建议设置为只读事务,提高查询效率。
在Spring 框架中可以设置定义哪些异常,进行事务的回滚:
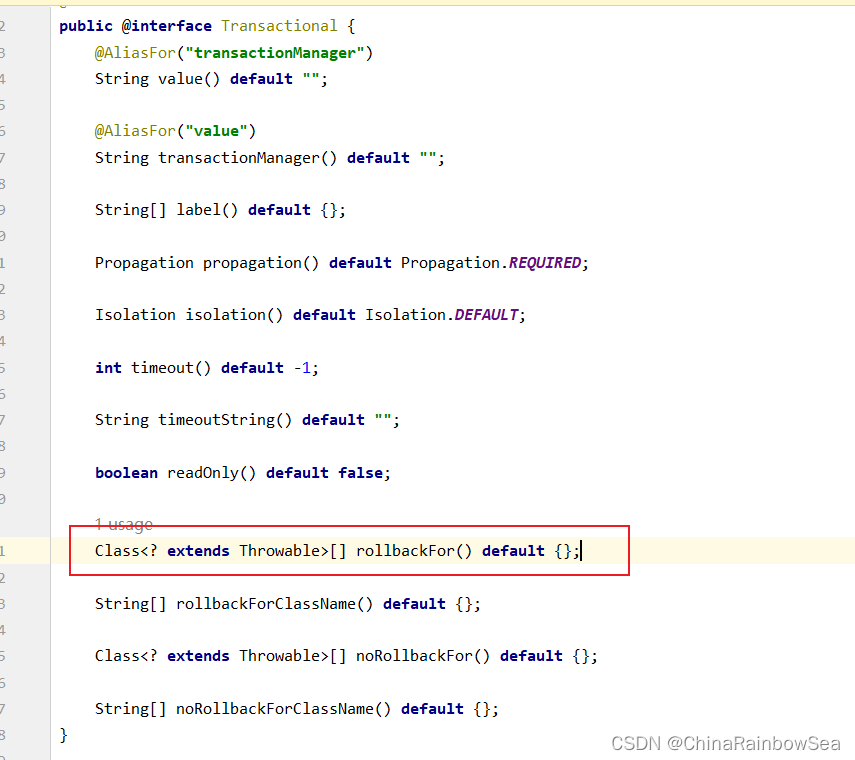
@Transactional(rollbackFor = XXX异常类.class)
@Transactional(rollbackFor = RuntimeException.class)
表示只有发生RuntimeException异常或该异常的子类异常才回滚。
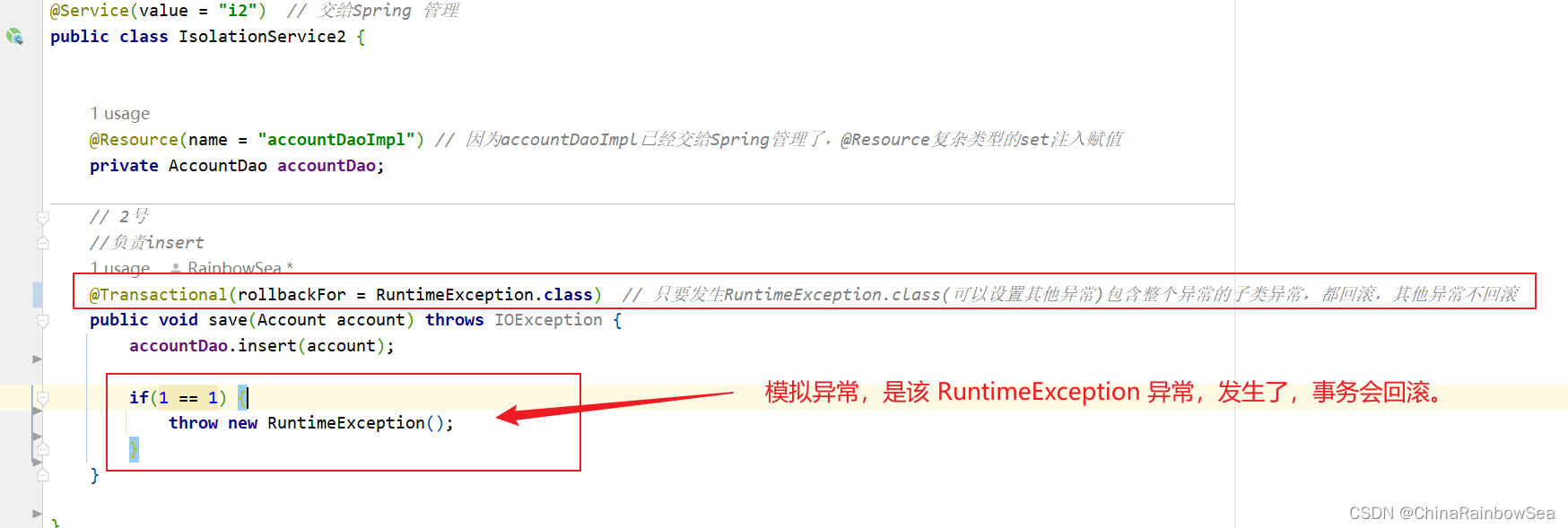
@Transactional(rollbackFor = RuntimeException.class) // 只要发生RuntimeException.class(可以设置其他异常)包含整个异常的子类异常,都回滚,其他异常不回滚
public void save(Account account) throws IOException {
accountDao.insert(account);
if(1 == 1) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
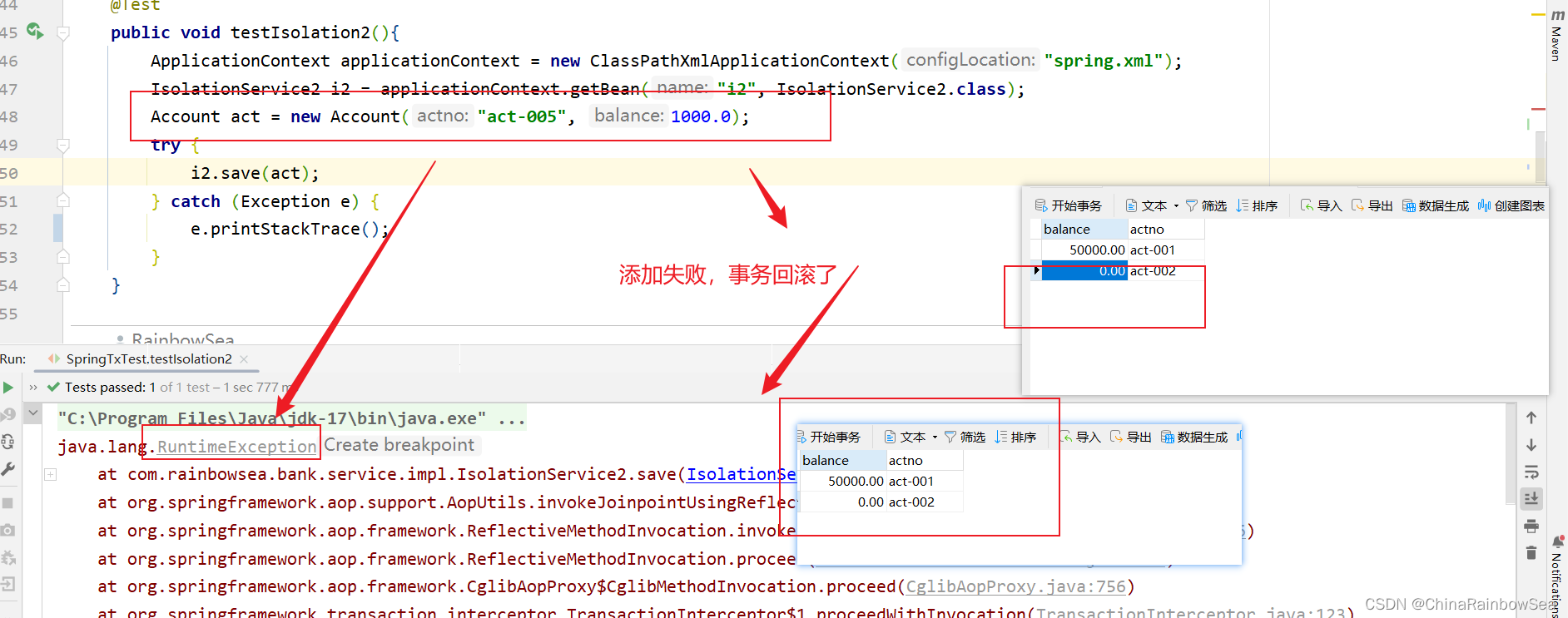
@Test
public void testIsolation2(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
IsolationService2 i2 = applicationContext.getBean("i2", IsolationService2.class);
Account act = new Account("act-005", 1000.0);
try {
i2.save(act);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
我们这次将异常换成:throw new IOException(); IO 异常不属于 RuntimeException 异常下的,发生该异常,不会回滚。

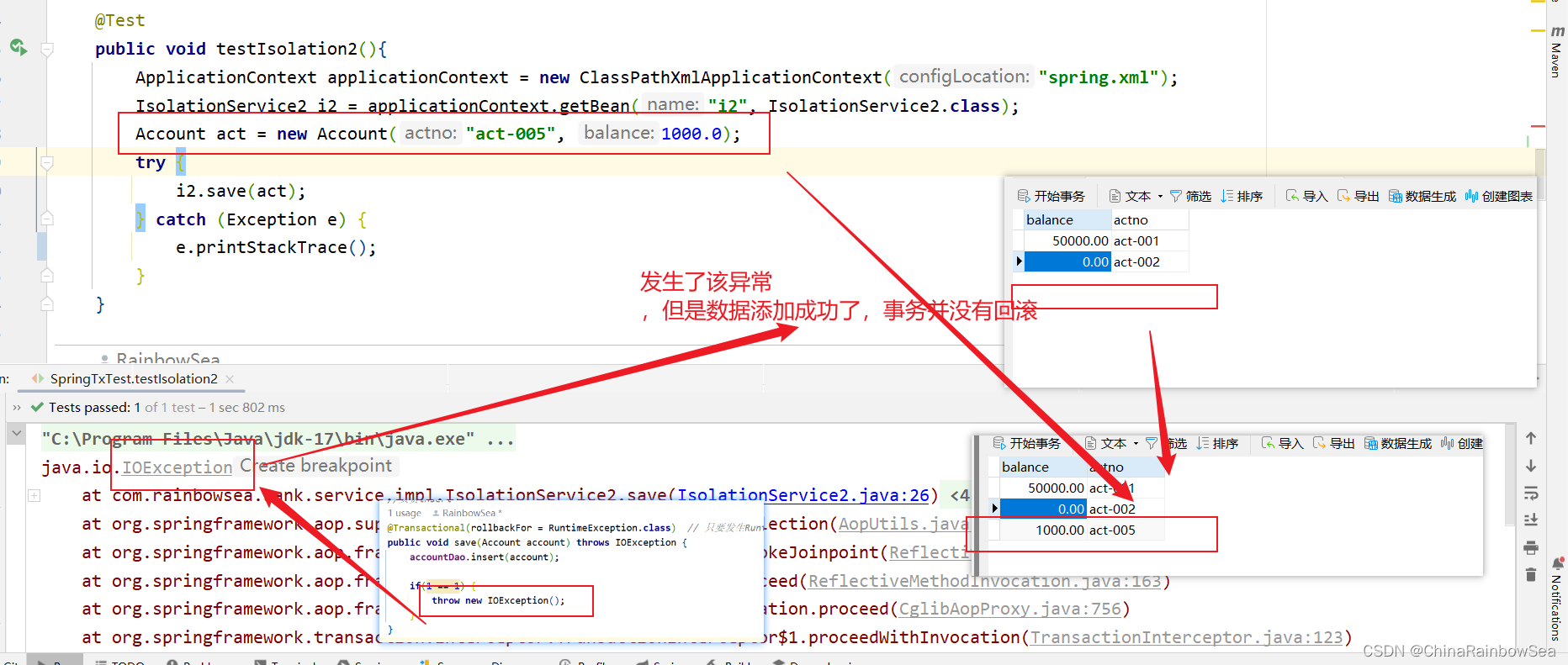
反过来,同样的在Spring 框架中可以设置定义哪些异常,不进行事务的回滚:
@Transactional(noRollbackFor = XXX异常类.class)
@Transactional(noRollbackFor = NullPointerException.class)
表示发生NullPointerException或该异常的子类异常不回滚,其他异常则回滚。
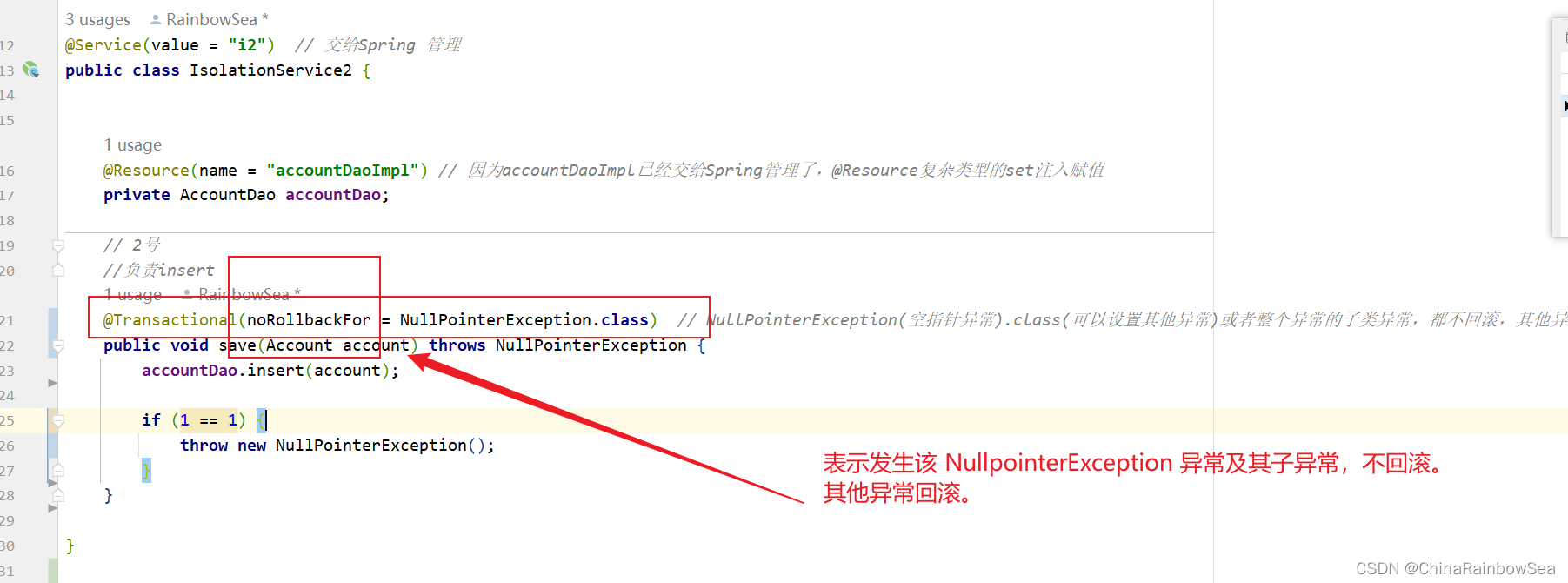
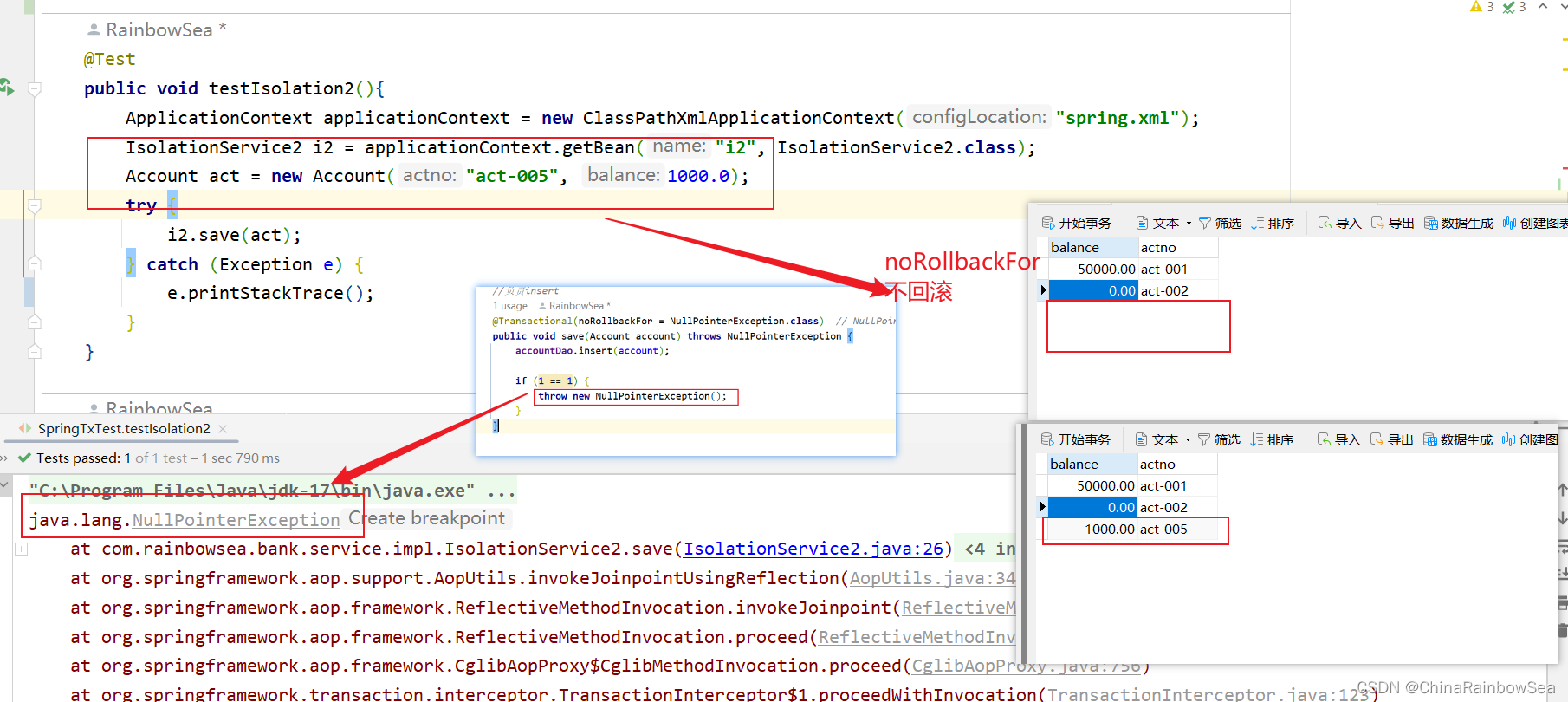
@Transactional(noRollbackFor = NullPointerException.class) // NullPointerException(空指针异常).class(可以设置其他异常)或者整个异常的子类异常,都不回滚,其他异常回滚
public void save(Account account) throws NullPointerException {
accountDao.insert(account);
if (1 == 1) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
}
我们这次将异常换成:throw new RuntimeException();; RUN 异常不属于 NullPointerException异常下的,发生该异常,会进行回滚。
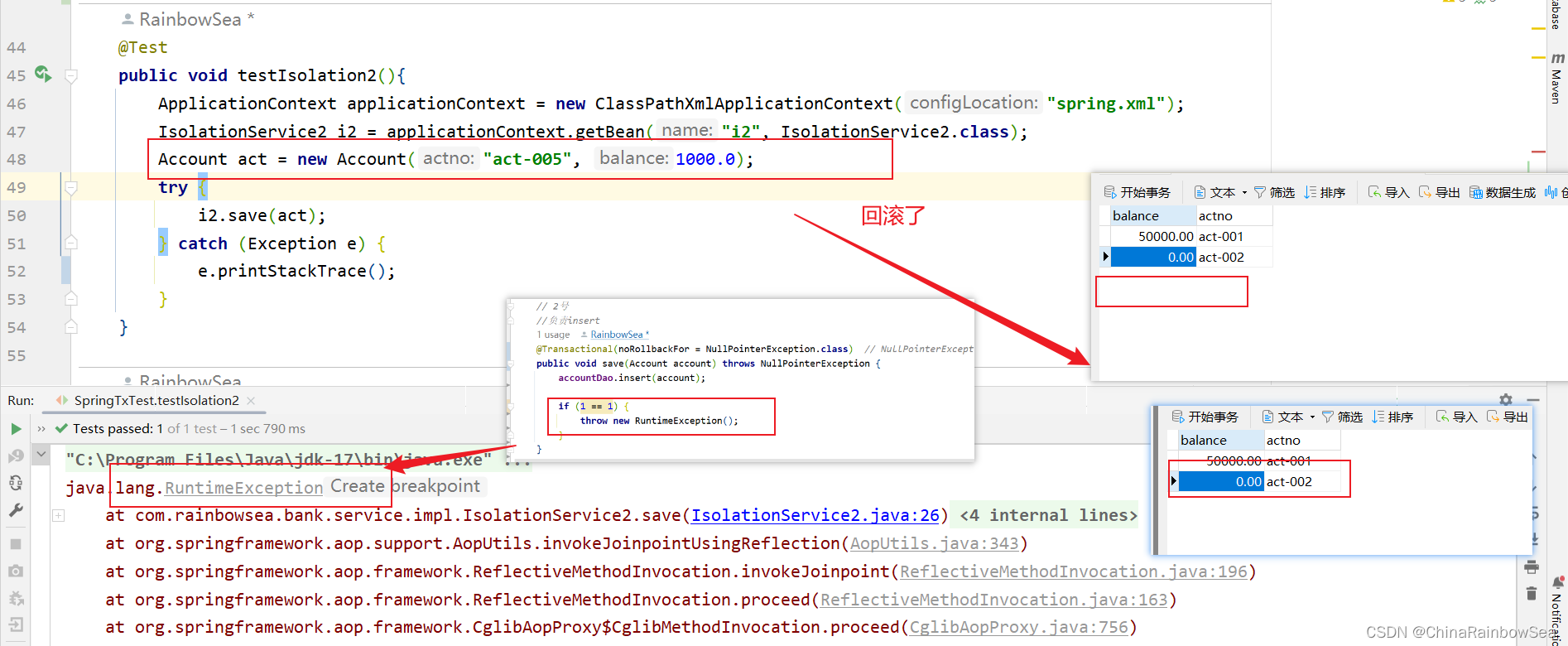
编写一个类来代替配置文件,代码如下:
注意:对于数据源以及JdbcTemplate, DataSourceTransactionManager 事务上的管理,我们可以使用 @Bean 进行注解式开发:
首先在配置类上,写明如下注解
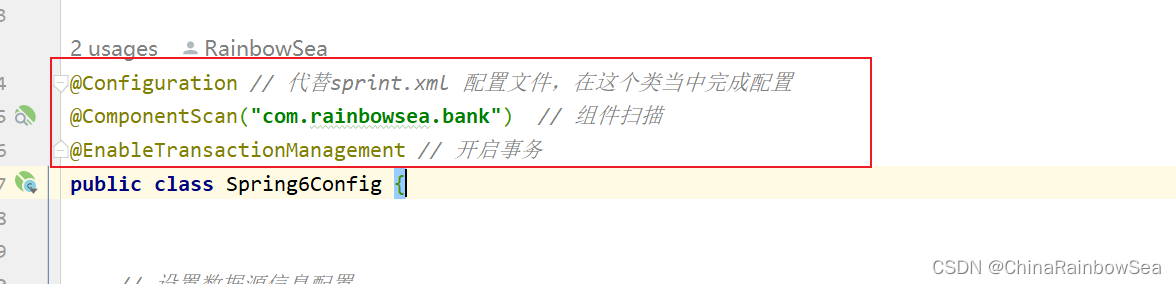
@Configuration // 代替sprint.xml 配置文件,在这个类当中完成配置
@ComponentScan("com.rainbowsea.bank") // 组件扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement // 开启事务
设置数据源信息配置:
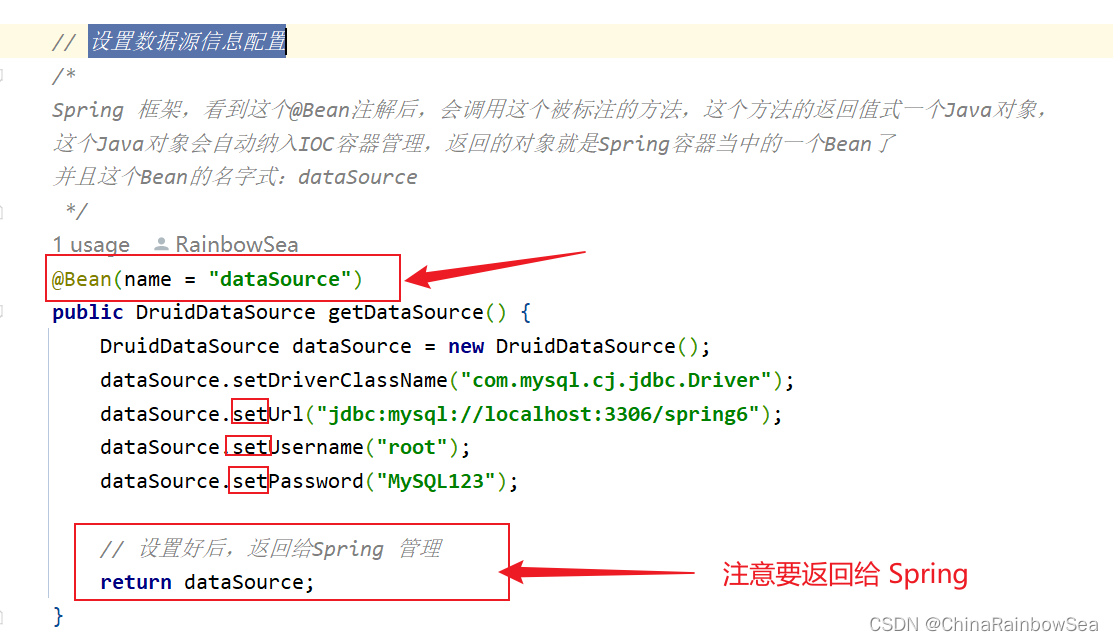
Spring 框架,看到这个 @Bean 注解后,会调用这个被标注的方法,这个方法的返回值是一个Java对象,这个Java对象会自动纳入 IOC容器管理,返回的对象就是Spring 容器当中的一个Bean 了。并且这个 Bean 的名字是:dataSource
同 getDataSource 方法()
@Bean(name = "xxxx")
使用 public DruidDataSource getDataSource() 方法。
// 设置数据源信息配置
/*
Spring 框架,看到这个@Bean注解后,会调用这个被标注的方法,这个方法的返回值式一个Java对象,
这个Java对象会自动纳入IOC容器管理,返回的对象就是Spring容器当中的一个Bean了
并且这个Bean的名字式:dataSource
*/
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
public DruidDataSource getDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("MySQL123");
// 设置好后,返回给Spring 管理
return dataSource;
}
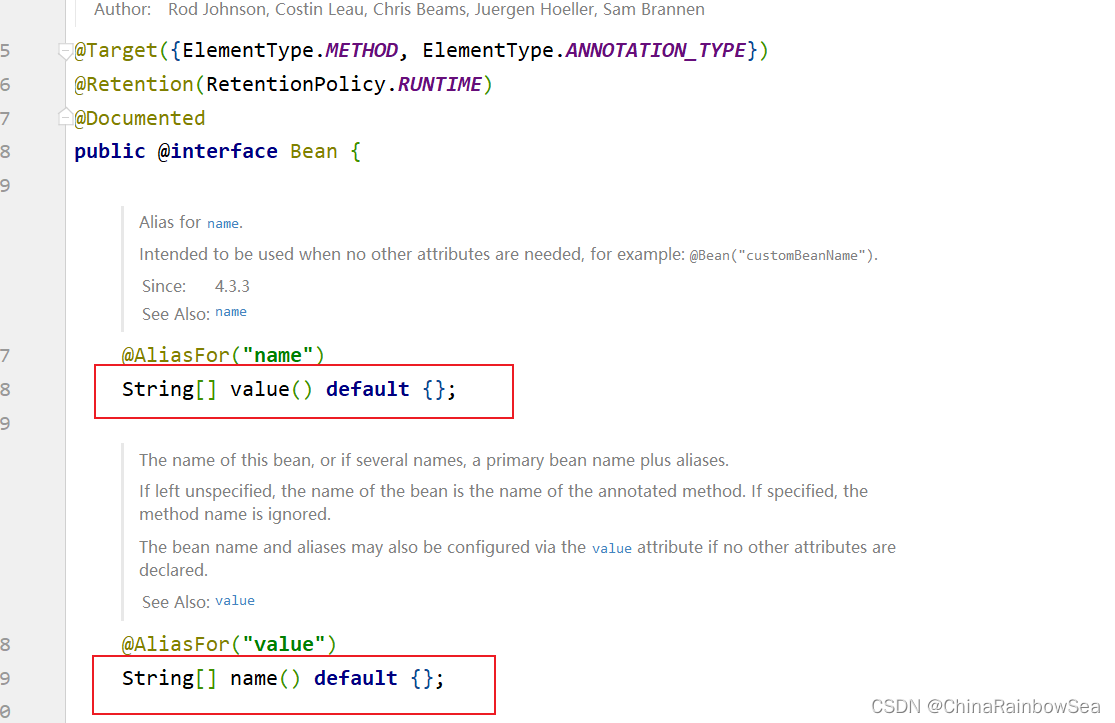
配置:JdbcTemplate Spring内置的 JDBC信息。用 public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) 方法
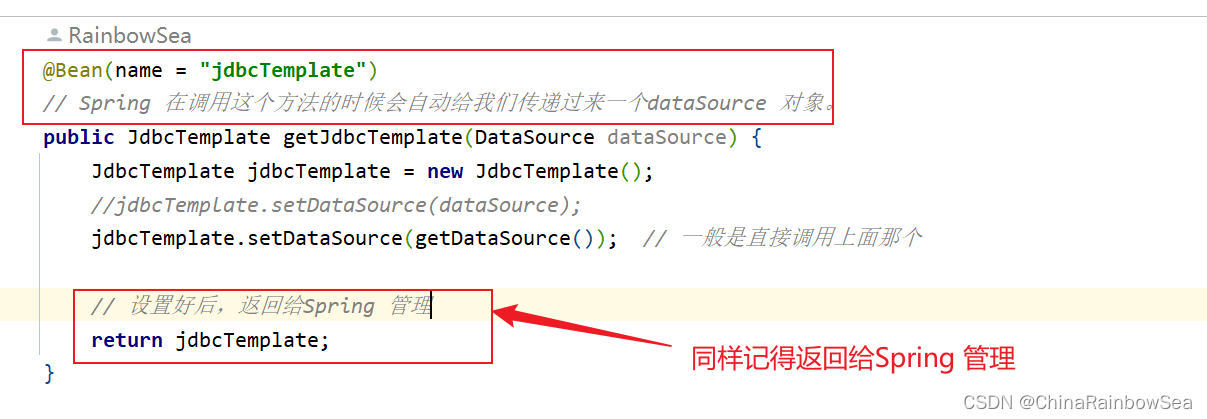
@Bean(name = "jdbcTemplate")
// Spring 在调用这个方法的时候会自动给我们传递过来一个dataSource 对象。
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
//jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(getDataSource()); // 一般是直接调用上面那个
// 设置好后,返回给Spring 管理
return jdbcTemplate;
}
配置事务管理上的配置信息:使用:public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource)
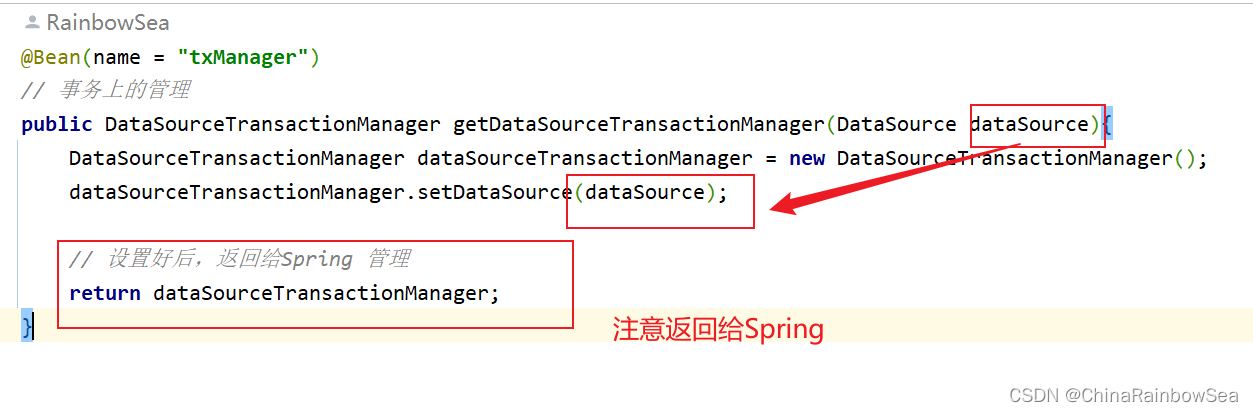
@Bean(name = "txManager")
// 事务上的管理
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
dataSourceTransactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 设置好后,返回给Spring 管理
return dataSourceTransactionManager;
}
完整的配置文件的信息的编写:
package com.rainbowsea.bank;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration // 代替sprint.xml 配置文件,在这个类当中完成配置
@ComponentScan("com.rainbowsea.bank") // 组件扫描
@EnableTransactionManagement // 开启事务
public class Spring6Config {
// 设置数据源信息配置
/*
Spring 框架,看到这个@Bean注解后,会调用这个被标注的方法,这个方法的返回值式一个Java对象,
这个Java对象会自动纳入IOC容器管理,返回的对象就是Spring容器当中的一个Bean了
并且这个Bean的名字式:dataSource
*/
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
public DruidDataSource getDataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6");
dataSource.setUsername("root");
dataSource.setPassword("MySQL123");
// 设置好后,返回给Spring 管理
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name = "jdbcTemplate")
// Spring 在调用这个方法的时候会自动给我们传递过来一个dataSource 对象。
public JdbcTemplate getJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource) {
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
//jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(dataSource);
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(getDataSource()); // 一般是直接调用上面那个
// 设置好后,返回给Spring 管理
return jdbcTemplate;
}
@Bean(name = "txManager")
// 事务上的管理
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDataSourceTransactionManager(DataSource dataSource){
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
dataSourceTransactionManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 设置好后,返回给Spring 管理
return dataSourceTransactionManager;
}
}
测试运行:
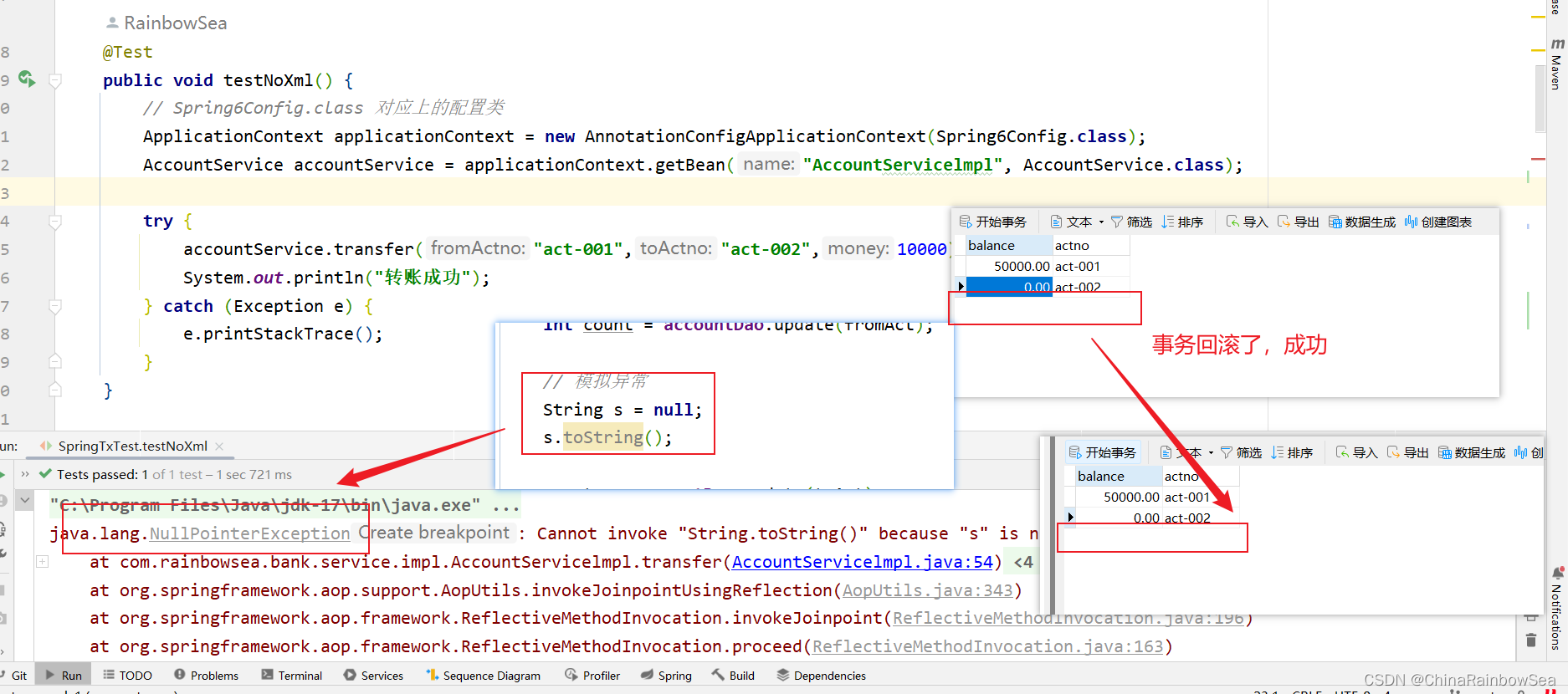
异常去了,再进行转账,测试是否成功。
public class SpringTxTest {
@Test
public void testNoXml() {
// Spring6Config.class 对应上的配置类
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Spring6Config.class);
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("AccountServicelmpl", AccountService.class);
try {
accountService.transfer("act-001","act-002",10000);
System.out.println("转账成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
首先添加相关依赖:记得添加aspectj的依赖:
在
pom.xml
当中配置相关的 jar 包
4.0.0
com.rainbowsea
spring6-014-tx-bank-xml
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
17
17
repository.spring.milestone
Spring Milestone Repository
https://repo.spring.io/milestone
org.springframework
spring-context
6.0.11
org.springframework
spring-aop
6.0.11
org.springframework
spring-jdbc
6.0.11
org.springframework
spring-aspects
6.0.11
mysql
mysql-connector-java
8.0.30
com.alibaba
druid
1.2.13
junit
junit
4.13.2
test
jakarta.annotation
jakarta.annotation-api
2.1.1
dao 包下的类:
package com.rainbowsea.bank.dao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* 根据账号查询账号信息
* @param actno
* @return
*/
Account selectByActno(String actno);
/**
* 更新账号信息
* @param account
* @return
*/
int update(Account account);
/**
* 保存账户信息
* @param act
* @return
*/
int insert(Account act);
}
bank.dao.impl 包下
package com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component(value = "accountDaoImpl")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
@Resource(name = "jdbcTemplate") // 该jdbcTemplate 已经纳入了Spring ICO 容器当中管理了,可以用@Resource根据
// 名称进行 非简单类型的 set 注入赋值
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public Account selectByActno(String actno) {
String sql = "select actno,balance from t_act where actno = ?";
// 查询
Account account = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Account.class), actno);
return account;
}
@Override
public int update(Account account) {
String sql = "update t_act set balance = ? where actno = ?";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, account.getBalance(), account.getActno());
return count;
}
@Override
public int insert(Account act) {
String sql = "insert into t_act(balance,actno) values(?,?)";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, act.getBalance(),act.getActno());
return count;
}
}
pojo 包下的类
package com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo;
public class Account {
private String actno;
private Double balance;
public Account() {
}
public Account(String actno, Double balance) {
this.actno = actno;
this.balance = balance;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"actno='" + actno + '\'' +
", balance=" + balance +
'}';
}
public String getActno() {
return actno;
}
public void setActno(String actno) {
this.actno = actno;
}
public Double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(Double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
service 包下
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
/**
* 业务接口
* 事务就是在这个接口下控制的
*/
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 转账业务方法
* @param fromActno 从这个账户转出
* @param toActno 转入这个账号
* @param money 转账金额
*/
void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno,double money);
}
bank.service.impl 包下的类
package com.rainbowsea.bank.service.impl;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.dao.AccountDao;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.pojo.Account;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.service.AccountService;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service(value = "accountServicelmpl")
public class AccountServicelmpl implements AccountService {
@Resource(name = "accountDaoImpl") // accountDaoImpl 已经被纳入了Spring IOC 容器管理了
// 所以可以使用 @Resource 进行非简单类型的 set 注入赋值
private AccountDao accountDao;
// 控制事务: 因为在这个方法中要完成所有的转账业务
@Override
public void transfer(String fromActno, String toActno, double money) {
// 第一步:开启事务
// 第二步:执行核心业务逻辑
// 查询转出账号的余额是否充足
Account fromAct = accountDao.selectByActno(fromActno);
if (fromAct.getBalance() < money) {
throw new RuntimeException("余额不足,转账失败");
// 第三步:回滚事务
}
// 余额充足
Account toAct = accountDao.selectByActno(toActno);
// 将内存中两个对象的余额先修改一下
fromAct.setBalance(fromAct.getBalance() - money);
toAct.setBalance(toAct.getBalance() + money);
// 数据库更新
int count = accountDao.update(fromAct);
// 模拟异常
//String s = null;
//s.toString();
count += accountDao.update(toAct);
if (count != 2) {
throw new RuntimeException("转账失败,联系银行");
// 第三步回滚事务
}
// 第三步:如果执行业务流程过程中,没有异常,提交事务
// 第四五:如果执行业务流程过程中,有异常,回滚事务
}
}
Spring.xml 配置文件如下:记得添加aop的命名空间。
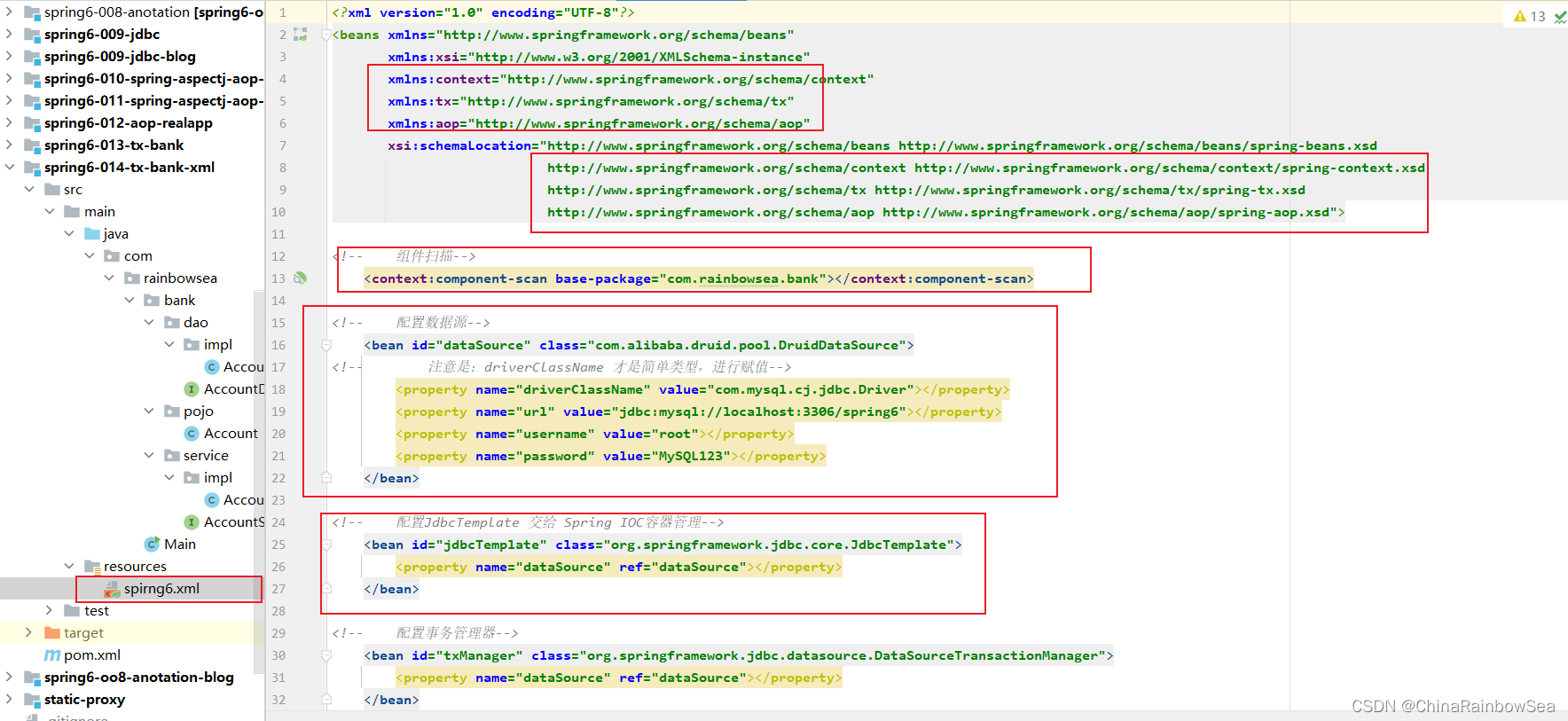
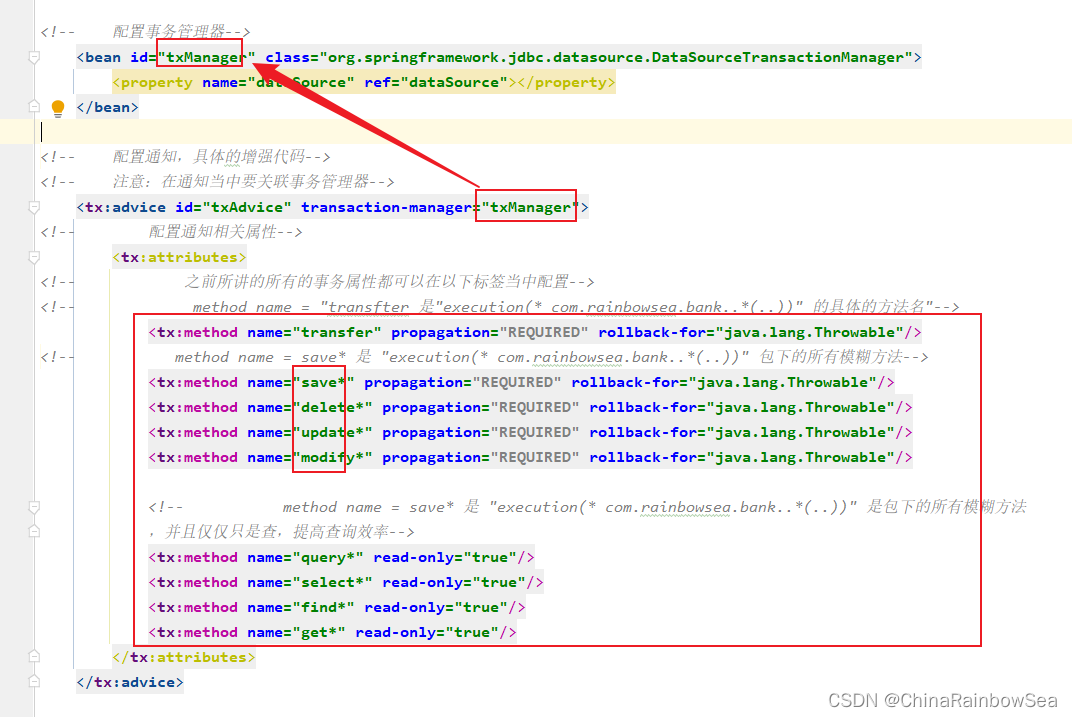
运行测试:
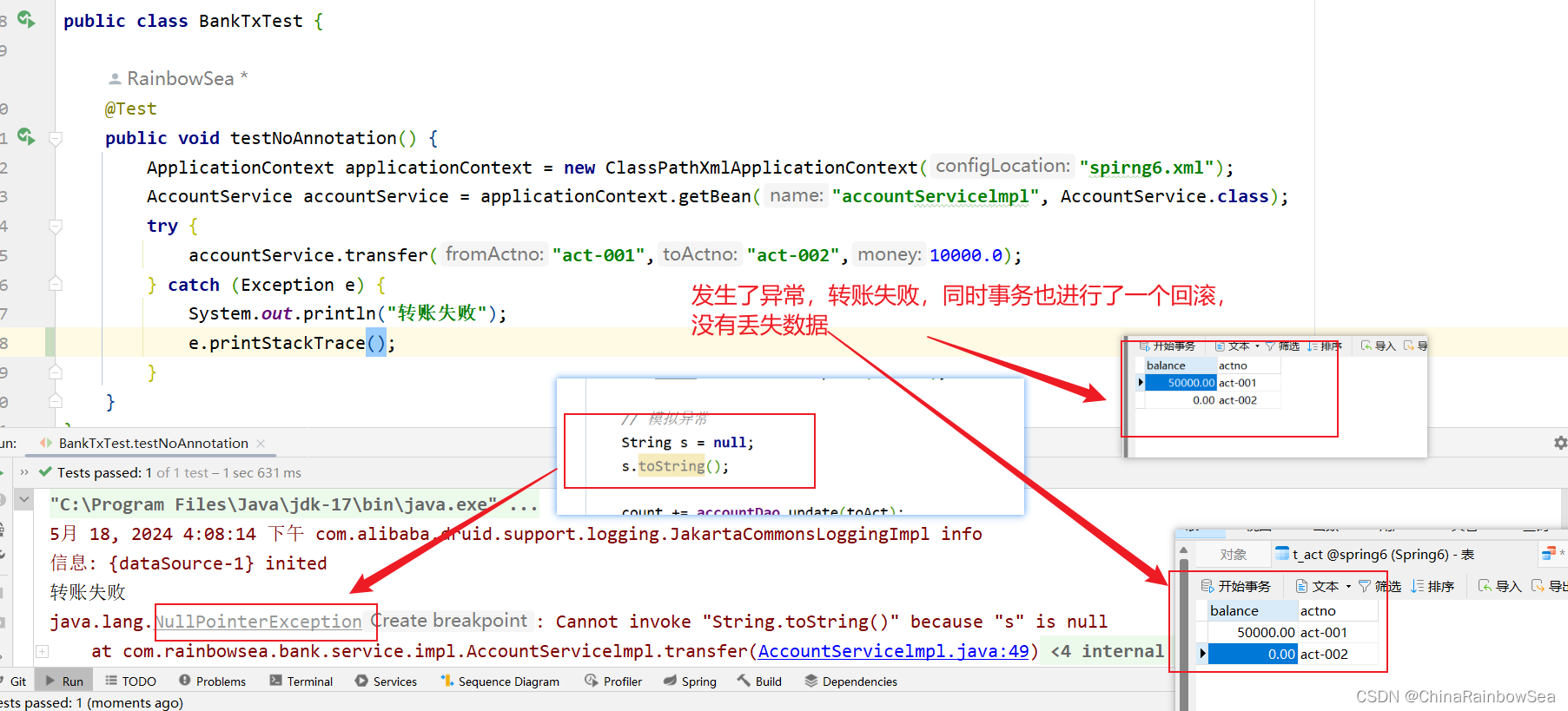
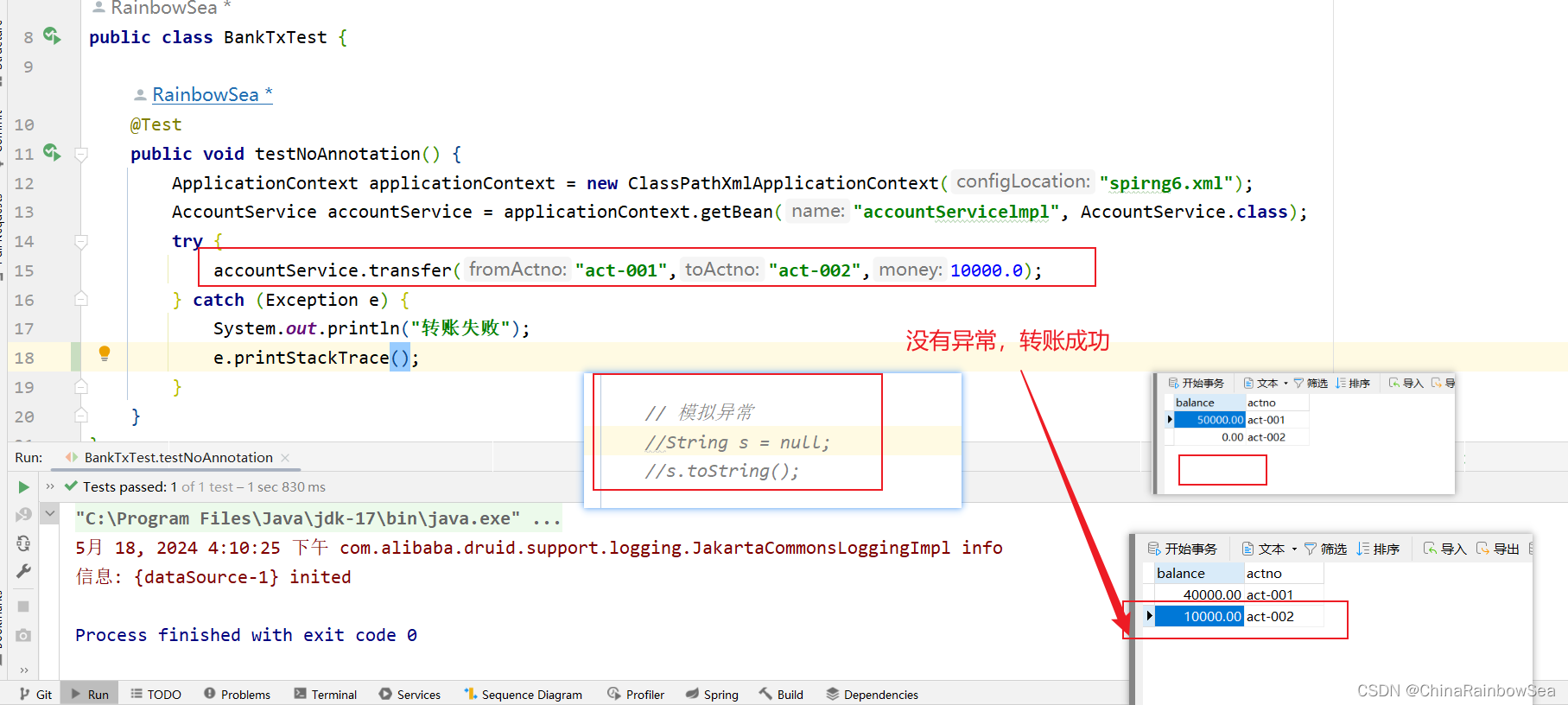
运行测试,没有异常,是否转账成功
package com.rianbowsea.spring6.test;
import com.rainbowsea.bank.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class BankTxTest {
@Test
public void testNoAnnotation() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spirng6.xml");
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountServicelmpl", AccountService.class);
try {
accountService.transfer("act-001","act-002",10000.0);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("转账失败");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 运行Spring 进行事务处理
- 基于注解方式
- 基于XML配置方式
- 事务上的理解
- 事务属性上的配置:
- 事务的传播行为
- 事务的隔离级别
- 事务的超时设置:超时设置是以最后一个 DML 语句的时间进行计时的(不包括最后一条DML语句后面的,不是 DML语句的业务上处理的运行的时间)
- 只读事务上的设置,提高查询效率
- 设置定义哪些异常回滚事务,不回滚事务
- 事务全注解式开发
- 声明事务之xml 实现方式
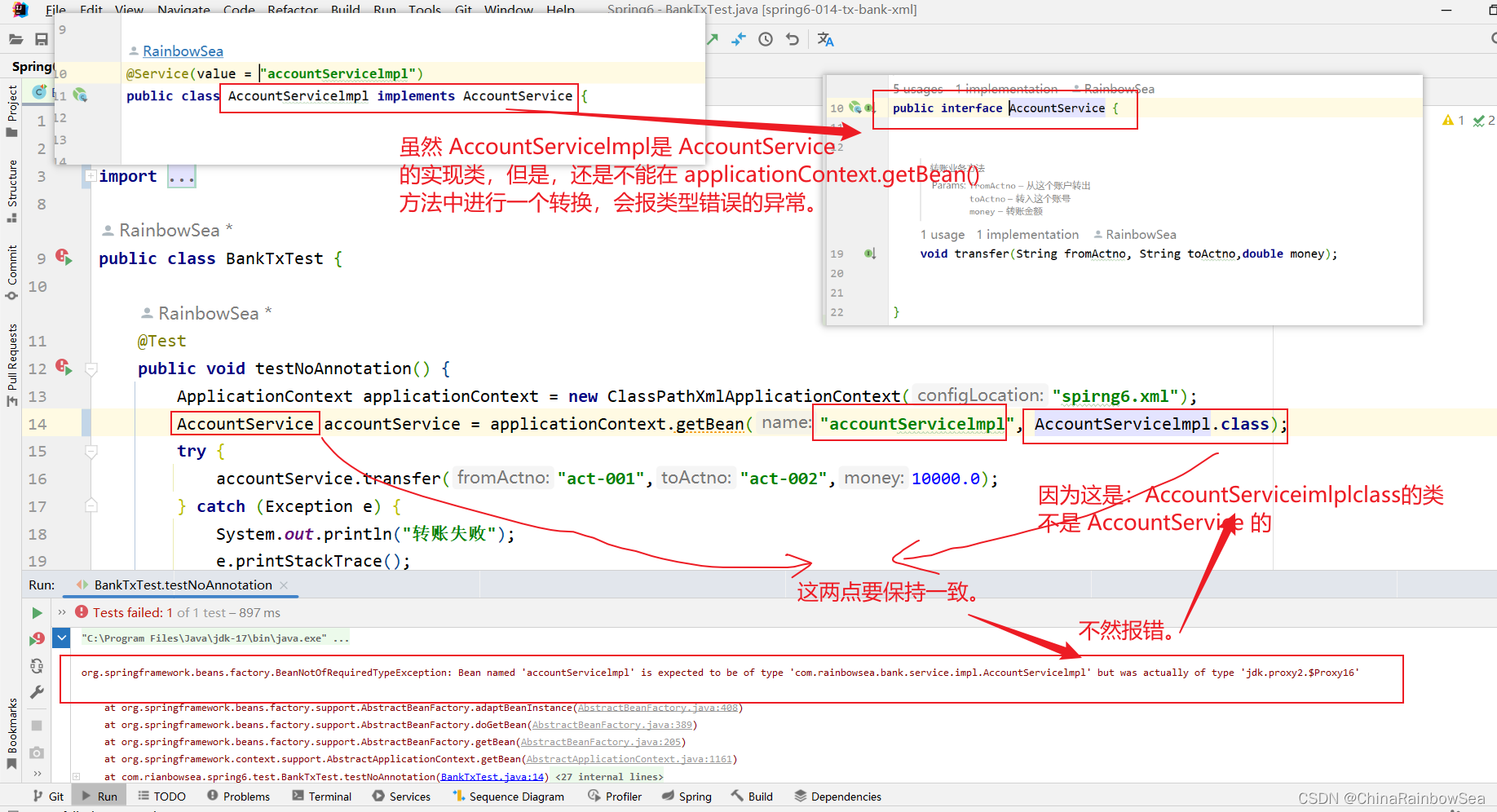
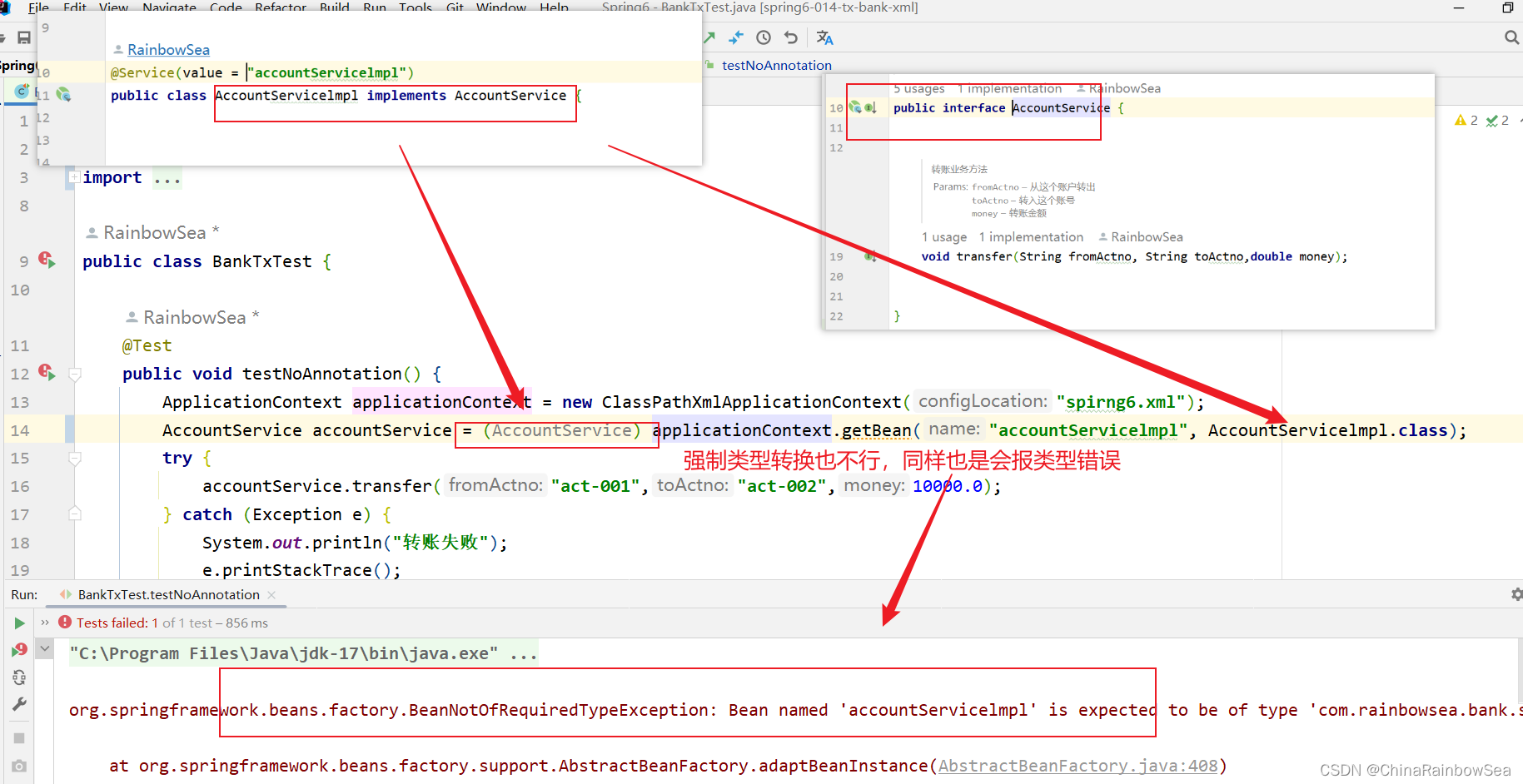
- 注意:在Spirng 当中,使用applicationContext.getBean(当中的,xxx.class) 要于返回值类型一致,不然会报类型不一致上的错误。如下:
“在这个最后的篇章中,我要表达我对每一位读者的感激之情。你们的关注和回复是我创作的动力源泉,我从你们身上吸取了无尽的灵感与勇气。我会将你们的鼓励留在心底,继续在其他的领域奋斗。感谢你们,我们总会在某个时刻再次相遇。”

热门资讯